BPMN 2.0 Introduction
BPMN 2.0 Training Material Most of those materials are based and heavily quote BPMN 2.0 Spec http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/2.0/
Note for NobleProg Trainers and Franchisees
Note that access to some new quizzes, questions and self-study materials has been restricted due to participation in OCEB v2 and will be released as a paid service.
Please contact bs@nobleprog.com for more details.
BPMN 2.0 Purpose。
- Provide a notation that is readily understandable by business and technical people
- Create a standardized bridge for the gap between the business process design and process implementation
- To ensure that XML languages designed for the execution of business processes, such as WSBPEL, can be visualized with a business-oriented notation.
- To standardize a business process model and notation in the face of many different modeling notations and viewpoints
- To provide a means of communicating process information to other businesses, users, managers and process implementers
- To exchange BPMN definitions (both domain model and diagram layout) between different tools
Audience of BPMN。
- Business users
- Business analysts
- Strategy analyst
- Quality managers
- Technical developers
- Process designers
- Developers
- Integrators
- Software, System and Enterprise Architects
Conformance。
Software based on spec
- software developed only partially matching compliance/conformance
Modeling Conformance
- Process modeling
- Choreography modelling
Execution Conformance
- Process Execution
- BPEL Process Execution
Tool can comply only to one of the above or any subset of them.
BPMN Complete Conformance complies to the all 4 above.
Sub-models within an end-to-end BPMN model 。
- Processes (Orchestration)
- Private non-executable (internal) BP
- Private executable (internal) BP
- Public Processes
- Choreographies
- Collaborations (can include Processes and Choreographies
- Conversations
BPMN and WSBPEL 。
- WSBPEL can organize complex Business Processes in a complex, disjointed, and unintuitive format that is handled very well by a software system (or a computer programmer)
- WSBPEL is hard to understand by the business analysts and managers
BPMN 2.0 compared to BPMN 1.2 。
- Formalizes the execution semantics for all BPMN elements
- Defines an extensibility mechanism
- Refines Event composition and correlation
- Extends the definition of human interactions
- Defines a Choreography model
BPMN Sub-models 。
- Orchestration
- Private non-executable (internal) Business Processes
- Private executable (internal) Business Processes
- Public Processes
- Choreographies
- Collaborations, which can include Processes and/or Choreographies
- A view of Conversations
Private (Internal) Business Process。
- Internal to a specific organization
- Other names:
- Workflow
- BPM Processes
- Orchestration of services
- Can be executable and non-executable
- Contained within a single Pool
- The flow of Messages can cross the Pool boundary to show the interactions that exist between separate private Business Processes
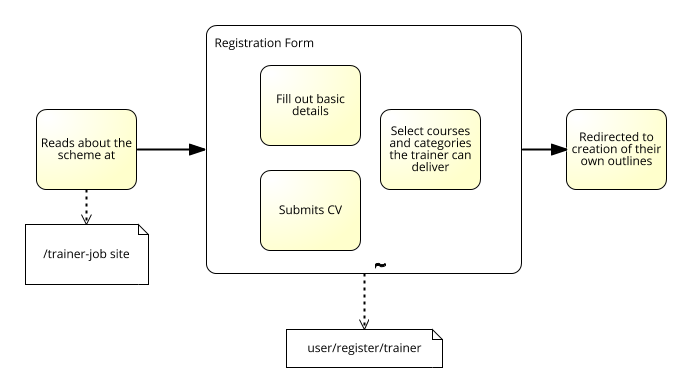
Public Process 。
- Represents the interactions between a private Business Process and another Process or Participant
- Only those Activities that are used to communicate to the other Participant(s) are included in the public Process
- All other “internal” Activities of the private Business Process are not shown
- Public Process shows to the outside world the Message Flows and the order of those Message Flows that are needed to interact with that Process
- Public Processes can be modeled separately or within a Collaboration to show the flow of Messages between the public Process Activities and other Participants
- Called “abstract” in BPMN 1.2.
- Public Process is orchestrated by the private processes (as oppose to Collaboration)
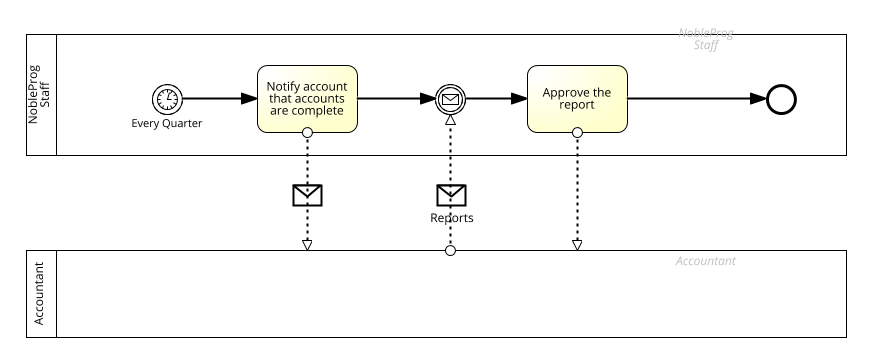
Collaboration。
- Depicts the interactions between two or more business entities
- Contains two or more Pools
- Can be shown as two or more public Processes communicating with each other
- The corresponding internal (executable) Processes are likely to have much more Activity and detail than what is shown in the public Processes.
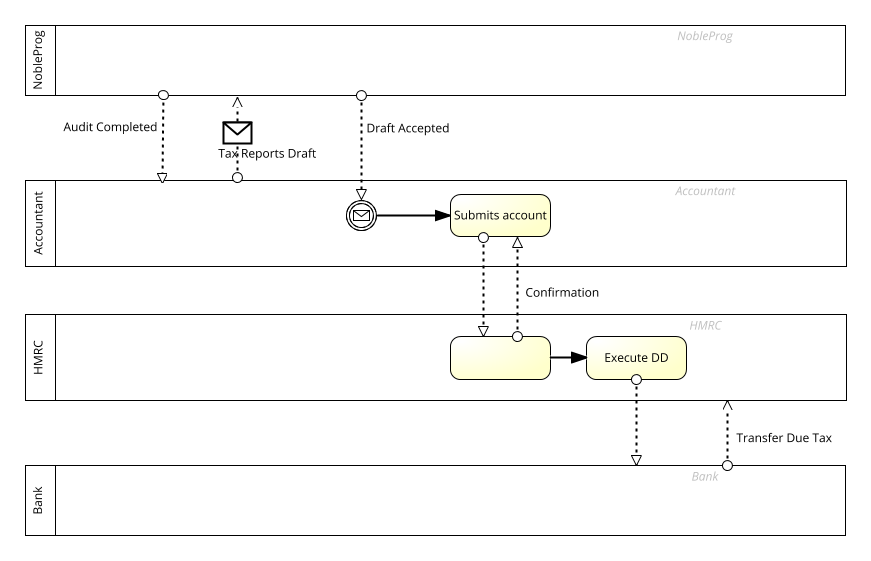
Choreography。
- Definition of the expected behavior
- B procedural contract between interacting Participants
- A self-contained Choreography have no Pools or Orchestration
- Choreography exists between Pools (or Participants)
- The Choreography Activities are interactions that represent a set (1 or more) of Message exchanges, which involves two or more Participants
- There is no central controller, responsible entity or observer of the Process
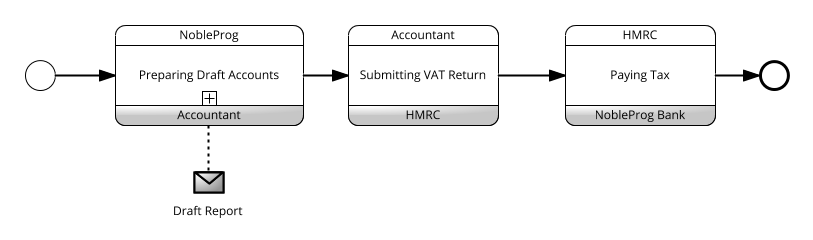
Conversation 。
- The Conversation diagram is a particular usage of and an informal description of a Collaboration diagram
- Pools of a Conversation usually do not contain a Process and a Choreography is usually not placed in between the Pools of a Conversation diagram
- A Conversation is the logical relation of Message exchanges
- Message exchanges are related to each other and reflect distinct business scenarios
- Conversation Diagram Provides a “bird’s eye” perspective of the different Conversations that relate to the domain
Quiz 。
BPMN_2.0_Introduction#Quiz_.E3.80.82
Quiz
