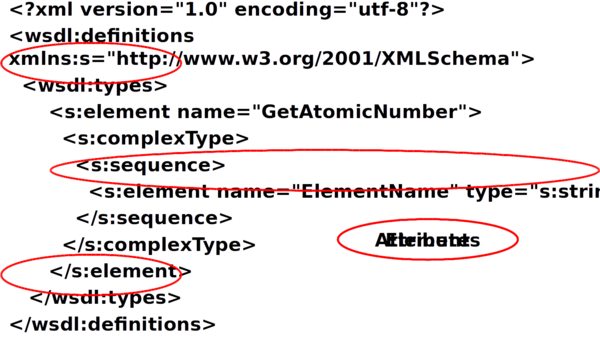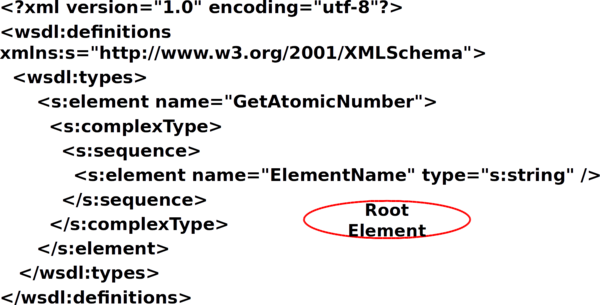XML
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Web Services Basics For Non-programmers
- author
- Pete George (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
Day One Schedule ⌘
- Introductions
- Service-Oriented Architecture
- Web Services Overview
- XML
- SOAP
XML ⌘
Learning Objectives
- To appreciate the advantages and disadvantages of using XML for Web services
- To understand the basic structure of an XML message
- To be aware of Xpath, XSD and XSLT
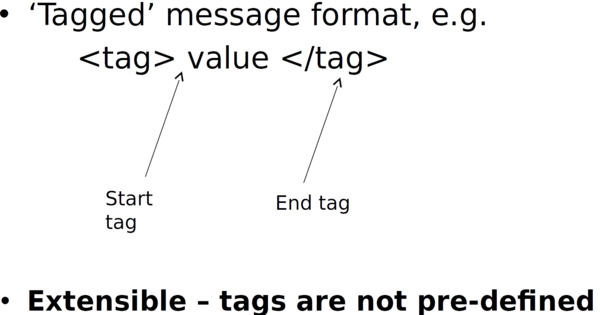
XML Messaging ⌘
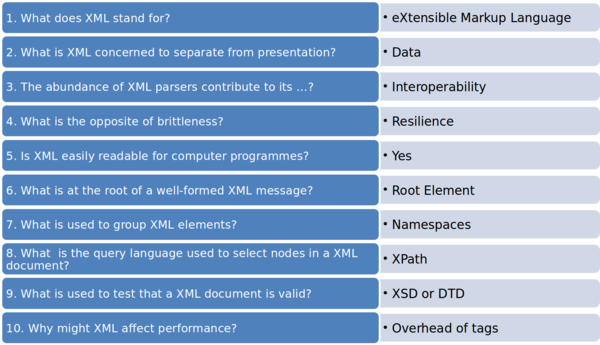
XML eXtensible Markup Language ⌘
- W3C Recommendation 1998
- Most common method for data exchange
eXtensible Markup Language ⌘
eXtensible Markup Language ⌘
- Markup language, like HTML
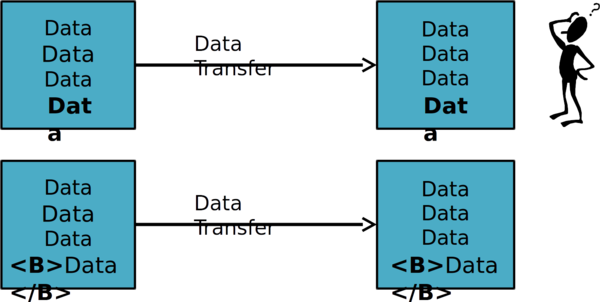
Why XML and Web Services? ⌘
- Data not presentation
- Interoperability
- Resilience
- Easily readable
Why XML and Web Services? ⌘
- Data not presentation
Why XML and Web Services? ⌘
- Interoperability
-Easy to agree XML format for data exchange
-High availability of XML parsers
-No need for low-level code to read/write data
Why XML and Web Services? ⌘
Why XML and Web Services? ⌘
- Easily readable
Easily Readable? ⌘
Elements and Attributes ⌘
- Elements, e.g.
<Users> some users </User>
- Attributes, e.g.
<user name=“Pete”> User1 </user> or <user name=“Pete”/>
Elements and Attributes ⌘
Root Element ⌘
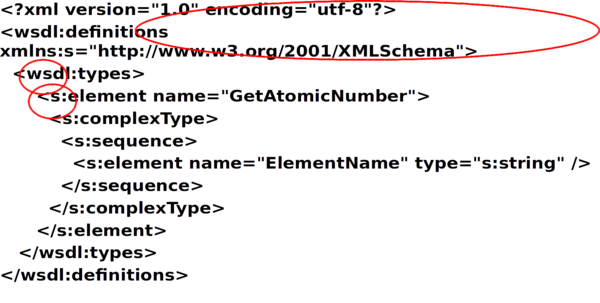
- Well-formed XML has one element at root
<rootElement> <anotherElement anAttribute=“some data”> </anotherElement> </rootElement>
Root Element ⌘
XML Prolog ⌘
- XML Prolog
<?xml version=“1.0”?>
-Optional, but usually declared
-May contain other information, e.g.
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“UTF-8”?>
XML Prolog ⌘
Namespaces ⌘
- Group XML elements together
- Declare namespace
xmlns=<URI>
-E.g. xmlns:PETE=http://pa-uk.net/etc <PETE:users >
Namespaces ⌘
- URI = Uniform Resource Identifier
-String that points to something
- Can be:
-URL = Uniform Resource Locator
-Specifies location of a resource
-[scheme]://[Domain]:[Port]/[Path]?[Querystring]#[FragmentId]
-URN = Uniform Resource Name
-Uniquely identifies something
-urn:[namespace identifier]:[namespace specific string]
Namespaces ⌘
Comments ⌘
- Comments can also be included
< !--This is a comment-- >
Entity References ⌘
- Illegal characters can be used by inserting entity references
& = &
< = <
> = >
“ = "
‘ = '
XPath ⌘
- XML Path Language
- Query language used to target specific elements or attributes
- Works like file system paths:
<users> <user name=“Pete” /> </users>
XPath = /Users/user
XPath ⌘
XML Document Definition ⌘
- Describe structure of XML document
- Used to test XML document is valid
- Used to author XML document in editor
- Document Type Definition (DTD)
-Widespread but on decline
-Not in XML format
XML Schema (XSD) ⌘
- Defines rules XML document must conform to be considered 'valid’
- Advantages over DTD:
-In XML format
-Namespace aware
-Data type aware
- defines elements/attributes containing values such as integers
XSLT ⌘
- Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations
- Transforms XML file into new XML file in new style
- Can transform XML into other forms, e.g. XHTML