Ubuntu Server Overview
- title
- Ubuntu Server Overview Training Course
- author
- Lukasz Sokolowski
Ubuntu Server Overview
Ubuntu Server Overview Training Materials
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
Introduction
- Overview
- Installation
- Ubuntu Server Edition
- Ubuntu and Hardware
- Package Management
Overview
Ubuntu
- For all people - usable even by disabled (anyhow)
- Connects people (opensource) - no matter what race, age, path, etc
- So my modified custom version of it's logo is.. (-;
Overview Con't - ..like that!
Installation
- Instant Ubuntu VMs
- multipass.run
- cloud-init.io
- multipass.run
- Manual
- ATM actual LTS Release Notes
- Automated
- maas.io
Ubuntu Server Edition
- Ubuntu versions
- Available support
- LTS vs standard edition
- Maintenance policy and life cycle
Ubuntu versions
- Every Oct and Apr, each year
- Funny codenames: Focal, Beaver, Tahr, etc
- Every 2y, stable and long support ver(for 5y)
- Choice between long-stable and features-full
Available support
- features-full - ATM: 21.04 and 21.10
- standard 9 months, no long-term, same EoL(9m)
- long-stable - ATM: 20.04.x, 18.04.x, 16.04.x, 14.04.x
- Long-Term Support 5y, EoL for 10y
LTS and standard edition
- Releases
- wiki.ubuntu.com/Releases
- ESM - Extended Security Maintenance
- Extendable subscription
- for LTS only, for 5y - free(private) or paid(enterprise)
- ubuntu.com/advantage
Maintenance policy and life cycle
- $ ua status
- debs, snaps, images, containers
- Version cycle
- ubuntu.com/about/release-cycle
Ubuntu and Hardware
- Checking compatibility with Ubuntu
- Available kernels and supported architectures
Checking compatibility with Ubuntu
- follows the requirements of the Linux kernel and the GNU tool-sets
- wiki.ubuntu.com/HardwareSupport
- ubuntu.com/certified
- wiki.ubuntu.com/Hardware_probe
- hwinfo, hw-probe, hwdata
sudo -E hw-probe -all -upload
- $ discover
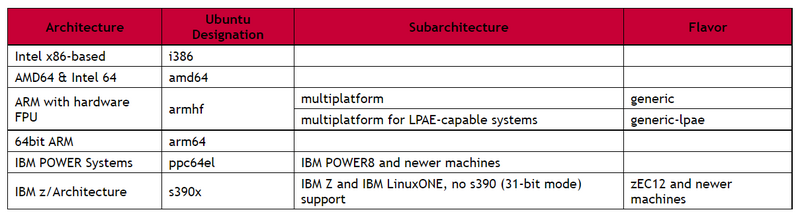
Available kernels and supported architectures
- help.ubuntu.com/lts/installation-guide/s390x/ch02s01.html
Package Management
- Dpkg VS apt-get VS snap(snapcraft.io)
- Available sources
- Adding new sources
- Alternative packet management systems (RPM, Yums, etc...) and dependencies
- Aptitude
- Automatic Updates
- Distribution Upgrades
Examples
# 'dpkg' VS 'apt' (or apt-get) VS 'snap'
sudo apt install mc
sudo snap install hello
sudo dpkg -i package_name.deb
# updating the index of packages
sudo apt update
# upgrading packages
sudo apt upgrade
# removing
sudo apt remove subversion*
# aptitude - menu-driven text-based front-end to 'apt'
sudo aptitude
Exercises
Install
- MariaDB via 'apt' command
- postgresql with 'snap'
- with 'dpkg' add nodejs
Sources
- Main - /etc/apt/sources.list
- Custom - /etc/apt/sources.list.d
- Adding new - manually, via commands
- mongoDB example
# Import the public key
wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-5.0.asc | sudo apt-key add -
# Creates a list file
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/5.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-5.0.list
# Refreshing the list
sudo apt update
RPM, Yum, etc
"Yes we can" - but don't!
- Doable but can have serious dependency issues
- It is always better to do it from sources instead and then make a deb package
- packaging.ubuntu.com/html/packaging-new-software.html
Automatic Updates
- If installed via snap - enabled by default (but slower run and separated form the rest of the server)
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
- Config - /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades
- Enabling - /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
- Automatic email when updates available - sudo apt install apticron
- Config - /etc/apticron/apticron.conf
Distro Upgrades
- To go for the next big ver, especially LTS
- sudo do-release-upgrade
- we should do it at least once in 5y, before the end of support for LTS
- To fully update existing release
- sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
- might be helpful, but does remove or install new things
- will be called by do-release-upgrade
Networking
- Network Configuration
- TCP/IP, IPv4 and IPv6
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) - server
- Time Synchronisation with NTP - depricated
- DPDK
Network Configuration
- Ethernet Interfaces - eno1, enp0s25 or kernel style eth#
- $ ip a
- $ sudo lshw -class network
- netplan config - match, set-name keys
- $ netplan info; netplan get all
- $ sudo ethtool eth3
IP Addressing
- Temporary assignment - ip command
- $ sudo ip addr add 10.102.66.200/24 dev enp0s25; ip link set dev enp0s25 up/down
- via DHCP or static IP
- use netplan config file and then $ sudo netplan apply
Name Resolution
- DNS Client Configuration - symlink with netplan
- /etc/resolv.conf -> ../run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf
- Static Hostnames - /etc/hosts
- Name Service Switch Configuration - /etc/nsswitch.conf
- Bridging - more advanced config, bridges: in /etc/netplan
- scenario1 - setting up a bridge with multiple network interfaces, then using a firewall to filter traffic between two network segments
- scenario2 - using bridge on a system with one interface to allow virtual machines direct access to the outside network
- networkd-dispatcher - for pre-up, post-up, etc. hook scripts
- netplan doesn't support hooks by deafult, like it was with ifupdown
DHCP server
- Configuration
- Manual allocation (MAC address)
- Dynamic allocation (address pool) - from scope(range)
- Automatic allocation - permanent assignment
- $ sudo apt install isc-dhcp-server
- Important related files
- /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
- /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server
Time sync
- timedatectl or timesyncd - they are part of systemd
- also chrony - chronyd and chronyc
- supports GPSD
- gpsd.gitlab.io/gpsd/hardware.html
- support for NTS(Network Time Security)
- supports GPSD
DPDK
- Data Plane Development Kit
- libraries and drivers for fast packet processing
- provide the EAL(Environment Abstraction Layer)
- hides the details of the environment and provides a standard programming interface
- Common use cases
- special solutions for instance network function virtualization
- advanced high-throughput network switching
- OpenVswitch-DPDK - built in client lib (openvswitch-switch-dpdk)
Remote Administration
- OpenSSH Server
- OpenLDAP Server
- Samba and LDAP
- Kerberos
OpenSSH Server
Tools for the remote control of networked computers and transfer of data between
- replaced insecured telnet and rcp
- ssh client calls sshd server via authenticated session
- secure and encrypted connection - plain passw, public key, Kerberos tickets
- clients: ssh, scp, etc
- packages: openssh-client, openssh-server
- configs: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- commands: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 ; ssh-copy-id username@remotehost ; ssh-import-id <username-on-remote-service>
OpenLDAP Server
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- for querying and modifying a X.500-based directory service running over TCP/IP
- Accesses directories
- directory - tree of data entries (DIT)
- entry - set of attributes, has unique identifier(DN)
- DN is based on RDN and it's parent entry's DN
- attribute - key and value(s), defined in objectClass(special attr)
- schema - consists of attrs and objectClasses
- Main config files: /etc/ldap/slapd.d ; /etc/ldap/schema
- Commands: ldapwhoami ; ldapadd ; ldapsearch ; ldappasswd ; ldapmodify
- Additional configs: add_content.ldif ; uid_index.ldif ; logging.ldif ; changerootpw.ldif
Samba and LDAP
- Samba 4 is best integrated with its own LDAP server in AD mode
- The NT4 mode - deprecated
More about Samba - later on.. (-;
Kerberos
Network authentication system based on the principal of a trusted third party
- Principal - users, computers, and services provided by servers
- Instances - service and special administrative principals
- Realms - domain or group our hosts and users belong to, uppercase, defult is DNS domain
- Key Distribution Center(KDC) - database, authentication, ticket granting; each realm >= 1 KDC
- Ticket Granting Ticket(TGT) - issued by the Authentication Server(AS), encrypted in user’s passw
- Ticket Granting Server(TGS) - issues service tickets to clients upon request
- Tickets - confirm the identity of user and service requested by the user
- Keytab Files - extracted from the KDC db, contain the encryption key for a service or host
Domain Name Service (DNS)
- Maps IPs with FQDN(fully qualified domain names)
- Configuration - name server
- $ sudo apt install bind9 dnsutils
- Common cases: caching nameserver, primary server, secondary server
- Can be all of them in the same time
- Config files
- global DNS options - /etc/bind/named.conf.options
- for our zones - /etc/bind/named.conf.local
- default (localhost, its reverse, root hints) - /etc/bind/named.conf.default-zones
- More here: ubuntu.com/server/docs/service-domain-name-service-dns
Security
- User Management
- Console Security
- Firewall
- AppArmor
- Certificates
- OpenVPN
- SSSD
User Management
- root disabled by default
- enabling - $ sudo passwd
- sudo - accountability, granular control
- group sudo, config /etc/sudoers
- Commands: adduser ; deluser ; chown ; chmod ; passwd ; addgroup ; delgroup
- Files: /home/username ; /etc/skel ; /etc/passwd ; /etc/group
- Remove/rename /home/username/.ssh/authorized_keys
- External user db auth - centralized (ldap, openid, cas, etc)
- Good password
Good password
- $ chage -l username
- min passw lenght
- passw expiration
- periodically forcing to change passw
- Good passw - Exercise
Console Security
- dis ctrl+alt+del
- $ sudo systemctl mask ctrl-alt-del.target ; sudo systemctl daemon-reload
- ssh captcha - libpam-captcha
- extensions - sentry over fail2ban(denyhosts, sshblacklist, etc)
Firewall
- Netfilter subsystem from Linux kernel
- managed with iptables
- Frontend tools can simplify it
- ufw - simple firewall config tool
- IP masquerading - private machine can access Internet through masquerade-machine
- doable via both: iptables and ufw
- Other tools - shorewall (advanced firewall)
- Logs - rules must come before terminating
AppArmor
- Linux Security Module implementation of name-based mandatory access controls
- installed and loaded by default
- uses profiles of an application to determine what files and permissions the application requires
- some packages will install their own profiles
- additional apparmor-profiles package
Certificates
- public-key cryptography
- public key encrypts, private key decrypts
- app traffic - with SSL(Secure Socket Layer) or TLS(Transport Layer Security)
- Example - apache with https
- Certificate - distributes public key and org
- digitally signed by CA(Certification Authority)
- self-signed (not recommended for prod envi)
- tools: openssl
- $ openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 2048
OpenVPN
- Virtual Private Networking (VPN)
- flexible, reliable and secure - originates from SSL/TLS VPN stacks
- Allows to set up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- uses SSL/TLS certificates for authentication
- and key exchange between the VPN server and clients
- routed or bridged VPN mode
- uses either UDP or TCP, default port 1194 (configurable) covers all communication
- support for all systems - Lin distros, OS X, Win, OpenWRT based WLAN routers, etc
SSSD
- System Security Services Daemon
- Collection of daemons that handle:
- authentication, authorization, and user and group information from a variety of network sources
- Its core supports - Active Directory, LDAP, Kerberos
- Provides PAM and NSS modules to integrate remote sources
- Allows remote users to login and be recognized as valid users, including group membership
- Allow for disconnected operation - cached when network failure, etc
Web Servers
- HTTPD - Apache2 Web Server
- LAMP - Linux, Apache, MySQL, Perl/Python/PHP
- Apache extensions like Tomcat, Kafka, etc
- PHP(5/7/8) - Scripting Language
- ATM, php8.1 - faster, more reliable, plenty of features (like JIT, Union Types, etc)
- Squid - Proxy Server
- full-featured web proxy cache server app
- caching SSL, DNS lookups, transparent caching
- caching protocols - ICP, HTCP, CARP, WCCP
- Ruby on Rails - open source web framework
- for developing database backed web applications
- optimized for sustainable productivity of the programmer
- lets the programmer to write code by favouring convention over configuration
- Nodejs based stacks like MEAN or MERN
Databases
- MySQL, MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
MySQL, MariaDB
- Fast, multi-threaded, multi-user, and robust db server
- Preferred for higher performance requirements
- Intended for mission-critical, heavy-load production systems and mass-deployed software
- Oracle took MySQL - here came MariaDB (-;
- Even faster, more performant and fully open-source
- DB engines - transparent to the end user
- MyISAM - fulltext data type, favours read-only workload, lacks journaling, locking only whole table
- InnoDB - ACID compliant, reliable transactions, locking on row level, journaled(more reliable data recovery)
- Commands: mysgl ; mysqld ; mysqldump ; mysqltuner
PostgreSQL
- Preferred for its attention to standards conformance, features, and extensibility
- Hybrid of relational and OOP approaches
- Streaming Replication
- continuously ships and applies the WAL XLOG records (Write-Ahead Log)
- keeps standby servers current
- Commands: psql ; postgresql
- Package with docs: postgresql-doc-12
Wiki Applications
- Moin Moin
- advanced, easy to use and extensible WikiEngine with a large community of users
- it is about collaboration on easily editable web pages
- MediaWiki
- php based collaboration and documentation platform
- powers Wikipedia and thousands of other websites, companies and organizations
- uses simple markup language - yet stil supports pure html
File Servers
- FTP Server
- downloading files between computers
- also uploading, but insecure - depricated
- Network File System (NFS)
- allows a system to share directories and files with others over a network
- locals use less disk space, same home dir on all machines, less removable medias
- CUPS - Print Server
- Common UNIX Printing System - freely available, portable printing layer
- uses Internet Printing Protocol (IPP), while supports large range of printers
- supports PostScript Printer Description (PPD) and auto-detection of network printers
Email Services
- Postfix
- default Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) in Ubuntu
- fast and secure, with flexibility in administration, compatible with the MTA sendmail
- Exim4
- Message Transfer Agent (MTA) developed at the University of Cambridge
- originally for Unix, can be installed in place of sendmail
- Dovecot Server
- Mail Delivery Agent, written with security primarily in mind
- It supports the major mailbox formats: mbox or Maildir, serves as IMAP or POP3
- Mailman
- open source program for managing electronic mail discussions and e-newsletter lists
- powerful, easy to install and maintain - all the Ubuntu mailing lists are using it
- Mail Filtering - modules like dovecot-sieve, dovecot-antispam
Version Control System
- Bazaar - free software sponsored by Canonical
- doc.bazaar.canonical.com/migration/en/why-switch-to-bazaar.html
- Subversion - based on CVS, improved a lot, centralized
- subversion.apache.org
- CVS Server - good(?) old grandpa (-;
- Mercurial - like git, but with more freedom (-:
- www.mercurial-scm.org
- GIT - "the stupid content tracker"
- distributed, fast, efficient, compressed
Windows Networking
Sharing network resources with Windows computers
- Samba File Server
- Facilitates sharing of files, folders, volumes
- Samba Print Server
- extends CUPS to share printers with Win cli
- Securing a Samba File and Print Server
- Identifying via file permissions, group policies, Kerberos authentication service
- needs additional package - libpam-winbind
- Samba as a Domain Controller - configured to appear as a WinNT4-style
- centralizes user and machine credentials, can work as PDC or BDC
- Samba Active Directory Integration
- Sharing vital information about the computers and users of the network - LDAP, MAD
- Likewise Open - old, depricated, insecure
Backups
- Shell Scripts
- Archive Rotation
- Bacula
- Rsnapshot
Shell Scripts
- File - backup.sh
- $ tar czf "/mnt/backup/$hostname-$day.tgz" "/home /var/spool/mail /etc /root /boot /opt"
- $ chmod u+x backup.sh
- one time - $ sudo ./backup.sh
- periodically - $ sudo crontab -e
# m h dom mon dow command 0 0 * * * bash /usr/local/bin/backup.sh
- restoring - $ cd / ; sudo tar -xzvf /mnt/backup/host-Monday.tgz
- Archive Rotation
- Rotating NFS Archives - grandfather-father-son rotation scheme (monthly-weekly-daily)
Bacula
- Backup, restore, and verify data across our network
- Cross-platform, supports - Lin, Win, MacOS
- Several components and services involved
- Director - main service, controls all the rest
- Console - pure text and GUI
- File(Client) - on each backed up machine, unswers to Director
- Storage - storage and recovery of data to the physical media
- Catalog - maintaining the file indexes and volume databases
- Monitor(only GUI so far) - monitoring of the Director, File and Storage daemons
Rsnapshot
- rsync-based filesystem snapshot utility
- incremental and scheduled backups of local and remote filesystems
- extensive use of hard links - low disk space used
- when remotely - needs SSH without password (OpenSSH)
Virtualization and Cloud Computing
- libvirt
- JeOS and vmbuilder - depricated, EoL
- packer.io - an alternative
- Quemu and KVM
- VirtualBox
- VMware
- EC2
- Containers - lxd, lxc
- Eucalyptus - old, replaced with OpenStack
libvirt
- Used to interface with different virtualization technologies
- kvm-ok - checks if our hardware supports the necessary virtualization extensions for KVM
- Virtual Machine Management - virsh, multipass, uvt, virt-*, openstack
- system and session scope
- migration - offline, live, postcopy
- Device Passthrough vs Hotplug
- can access Qemu monitor
- Huge Pages - allocation, usage
- Apparmor isolation
- Sharing files between Host <=> Guest
Quemu and KVM
- machine emulator
- can run operating systems and programs for one machine on a different machine
- Mostly used as virtualizer with KVM kernel components
- utilizes the virtualization technology of the hardware to virtualize guests
- Upgrading the machine type
- Usage for microvms
VirtualBox
x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization - enterprise and home use
- lots of features
- backed by Oracle and huge community
- high performance
- open source via GPL2
- runs on Win, Lin, Mac, Sol
- offers guests in above and also OS/2, OpenBSD
- guest-additions (mostly for GUIs)
VMware
Not only virtualization
- Platform for applications
- multi-cloud (Telco, etc)
- Networking, security
- Workspace - any-*
EC2
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2)
- humongous web service, mostly for developers
- provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud
- complete control of computing resources
- supports macOS
- Intel, AMD, and Arm-based processors
- ATM: 25 regions and 81 availability zones globally
Containers - lxd, lxc
- lxd - like libvirt
- lightervisor - lightweight container hypervisor
- creates and administers "containers" on a local system
- LXD API deals with ‘remotes’
- uses LXC under the covers
- commands: lxd init ; lxc launch ; lxc image list(info) ; lxc exec ; lxc config ; lxc-remote
- lxc - like QEMU
- Containers are a lightweight virtualization - an enhanced chroot, no full virtualization
- Do not emulate hardware, share the same operating system as the host
- similar to Solaris zones or BSD jails
- implementations in Linux - vserver and OpenVZ ("fathers" of containers)
- commands: lxc-create ; lxc-ls ; lxc-start(stop) ; lxc-info ; lxc-destroy ; lxc-attach
Other
- Keeping /etc under Version Control System
- Block Device Replication
Tools
- byobu
- etckeeper
- munin
- nagios
- pam_motd
- Puppet
Byobu
- xterm multiplexor
- acts as a wrapper to screen or tmux(default)
- multiple shells in one terminal
- more user-friendly
etckeeper
- industry best practice
- stores the contents of /etc in VCS repo (default is GIT)
- integrates with APT
- automatic commits of changes in packages
sudo apt install etckeeper
munin
- networked resource monitoring tool
- helps analyze resource trends and performance issues
- plug and play
- no need to configure - default inst. provides a lot of graphs
nagios
Monitoring of
- Network
- overloaded data links or network connections, routers, switches, etc
- availability, uptime and response time - all in a variety of visual representations and reports
- Server - for Win and Lin
- supports agent-based and agentless monitoring
- above 5000 different addons from community
- Application - Win, Lin, UNIX, Web
- detects application, service, or process problems
- takes action to eliminate downtime for our application users
pam_motd
After logging shows the informative Message Of The Day (MOTD)
- landscape-common - displaying core system data: cpu, memory, disk space, etc
- update-notifier-common - available package updates, impending filesystem checks (fsck), and required reboots
- weather-util, etc
Puppet
- cross platform framework enabling system admins to perform common tasks using code
- installing new software, checking file permissions, updating user accounts, etc
- Useful during the initial inst. of a system, also throughout the system’s entire life cycle
- Mostly used in a client/server configuration
Block Device Replication
Ubuntu HA - DRBD
- Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD)
- mirrors block devices between multiple hosts
- transparent to other applications
- Mirrors - any block device hard disks, partitions, RAID devices, logical volumes, etc
sudo apt install drbd8-utils
THE END
Summary - Ubuntu
- Try it and have fun! (-;
- Enjoy the fearless world of debian-based distro
- Stable, safe and yet modern system
- For PL-guys check: ubuntu.pl
Resources
Based on (mostly):
- ubuntu.com/server/docs