Statistics for Decision Makers - 06.01 - Research Design - Scientific Method
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="。" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" footer="www.NobleProg.co.uk" subfooter="Training Courses Worldwide">
- title
- 06.01 - Research Design - Scientific Method
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (NobleProg Ltd) bs@nobleprog.co.uk
</slideshow>
The Scientific Method。
- Depends on empirical data.
- The data must be collected systematically.
- Does not require manipulating variables and observing the results (e.g. astronomy).
- Theories in science can never be proved since one can never be 100% certain that a new empirical finding inconsistent with the theory will not be found.
- Scientific theories must be potentially disconfirmable.
- A scientific theory should lead to testable hypotheses.
- If a hypothesis is disconfirmed, then the theory from which the hypothesis was deduced is incorrect.
Example
Theory。
- The secondary reinforcement theory of attachment
- An infant becomes attached to its parent by means of a pairing of the parent with a primary reinforcer (food).
- It is through this "secondary reinforcement" that the child-parent bond forms.
- Disconfirmation experiment
- The infant monkeys were fed by a surrogate wire mother while a surrogate cloth mother was available.
- The infant monkeys formed no attachment to the wire monkeys and frequently clung to the cloth surrogate mothers.
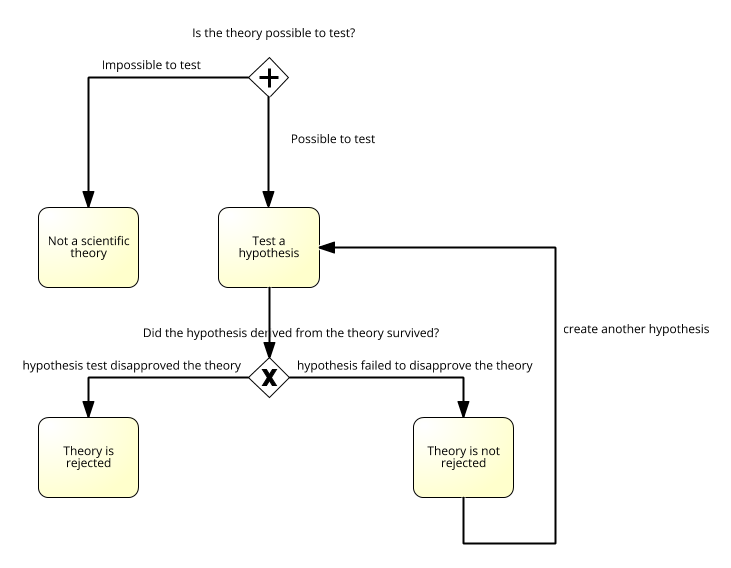
Scientific Proof。
|
|
Theories and Hypothesis。
- The method of investigation in which a hypothesis is developed from a theory and then confirmed or disconfirmed involves deductive reasoning.
- Disconfirming a hypothesis deduced from a theory disconfirms the theory.
- The theory will probably be modified to accommodate the inconsistent finding.
From Theory to Hypothesis - Hypothesis。
- A hypothesis is an educated guess, based on observation.
- It can be supported or refuted through experimentation or observation.
- A hypothesis can be disproven, but not proven to be true.
- You may hypothesize that Gmail is the fastest mail service in the world.
- The hypothesis can be disproven if a faster mail service is found : On the other hand, you cannot prove the hypothesis.
- Even if you have never found a faster mail service after trying a thousand different mail services, there might be one you haven't tried that could be different.
From Theory to Hypothesis - Theory。
- A scientific theory summarizes a hypothesis or a group of hypotheses that have been supported with repeated testing.
- A theory is valid as long as there is no evidence to dispute it.
- Theories can be disproven.
- Basically, if evidence accumulates to support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis can become accepted as a good explanation of a phenomenon.
- A theory is an accepted hypothesis.
Example。
(Credit: CERN)
- The Higgs Field was hypothesised for long time.
- During the experiment in CERN in 2013 it has been tentatively confirmed.
- The Higgs Field became a theory from then on.
- If further experiment disaprove this, the Higgs Field Theory will no longer be valid.
Things which are not hypotheses。
- The hypothesis or theory has to be falsifiable.
- If the statement cannot be falisfied in the first place, it cannot be a theory.
- The non-existence of God, as defined by most religions, cannot be disproven as it is impossible to create an experiment in which we can check that God definitely doesn't exist.
- Therefore the existence of God can be proven, for example, by finding one directly.
Things which are not hypotheses。
Example 2
- The non-existence of fault in a computer program usually cannot be proven as there are too many different circumstances under which code can fail.
- On the other hand, the existence of a computer bug can be proven by finding one.
Things which are not hypotheses。
- It cannot be proven that gaining a monopoly in a specific market is impossible.
- It is possible to find a company which has a monopoly in a specific market.
Where do theories come from? - Induction vs Deduction。
- The method of investigation in which a hypothesis is developed from a theory and then confirmed or disconfirmed involves deductive reasoning.
- Deductive reasoning does not explain where the theory came from in the first place.
- A theory is developed by a scientist who is aware of many empirical findings on a topic of interest.
- Induction is a process through which the scientist develops a way to explain the findings.
- Induction is not really well understood.
- Therefore science is still half-science half-art [sic!].
Decision Maker Dilemma。
- Theories in the business world change more often than in science.
- Therefore, proving anything is more difficult and the evidence is more ephemeral.
- Despite this, a manager who knows what can and what cannot be proven can have an edge compared to a competitor wasting their time on trying to prove something which cannot be proven or disproving something which cannot be disproven.
Quiz。
Quiz