Product Design with - Agile - Lean - Kanban
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" subfooter >
- title
- Product Design with - Agile - Lean - Kanban
- author
- (安博)Bernard Szlachta (anbo@altran-beyondsoft.com)
- logo
- subfooter
- Bernard Szlachta 2016 All Rights Reserved - Template:Date
</slideshow>
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
My and Agile/Lean/Kanban ⌘
- Mostly software
- Nagravision - security devices, TV boxes
- Hardware + Low level software (not snazy website)
Problems ⌘
- Miss deadlines
- Nothing comes out
- overbudget
- Unused funcioanltiy
- Due to requirements changed
- Requirements where never clear
Examples of Lean Design in Product (not only software) ⌘
- Well Documented
- Lean in Design (WikiSpeed) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x8jdx-lf2Dw
- My Experience
- Nagravision
Lean 精益 ⌘
What is Lean ⌘
Types of Lean ⌘
- Lean Manufacturing (Toyota)
- Lean in Design
- Lean in Software
LEAN Thinking 精益思想 ⌘
Five Principles of LEAN ⌘
James P. Womack, Daniel T. Jones "Lean Thinking"
- 价值观 (Value)
- 价值流 (Value Stream)
- 流动 (Flow)
- 拉动 (Pull)
- 尽善尽美 (Perfection)
Using Lean in R&D ⌘
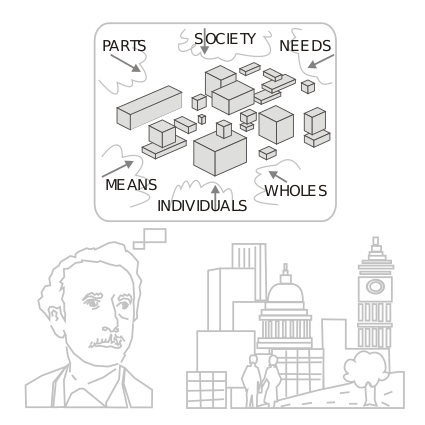
System Thinking (from Deming) ⌘
System Thinking Tenets ⌘
- Interdependence (nothing is independent)
- Holism (analysis of a interdpendent components as a whole, not as separate subsystem)
- Goal Seeking - the System has a goal
- Inputs and Outputs - determin the boundary of a system
- Hierarchy
Usage ⌘
- Business Optimization (Lean, JIT, Supply Chain, etc...)
- Impact analysis (Tsunami in Japan on business in the UK)
- Engineering optimization (e.g. remove printing invoices rather than improve process of printing them)
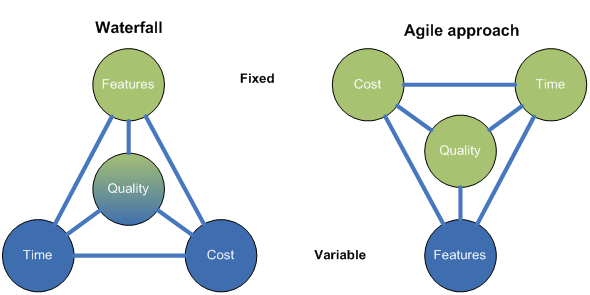
Plan driven vs. Value driven ⌘
加农炮 vs 导弹 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Missile#/media/File:V-2_lift-off.jpg
Team Power ⌘
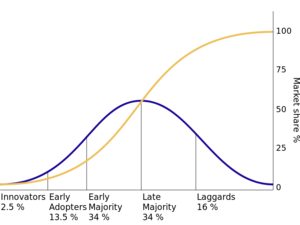
Innovation curve ⌘
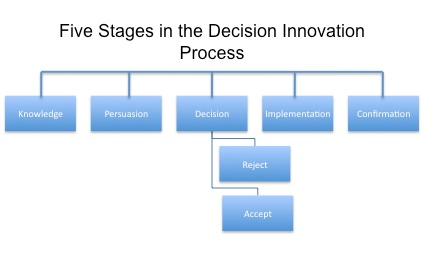
Decision Innovation Process ⌘
More: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffusion_of_innovations
Comparison of iterative methodologies ⌘
Why things go wrong ⌘
The LEAN approach ⌘
Lean 精益生产 ⌘
- 消除浪费
- 增强学习
- 尽量延迟决定
- 尽快发布
- 下放权力
- 嵌入质量
- 全局优化
敏捷方法 Agile ⌘
敏捷软件开发宣言
- 个体和互动 高于 流程和工具
- 工作的软件 高于 详尽的文档
- 客户合作 高于 合同谈判
- 响应变化 高于 跟进计划
也就是说,尽管右项有其价值,我们更重视左项的价值。
http://www.agilemanifesto.org/
Agile Inverted Triangle ⌘
Successful Project ⌘
- Successful project is not necessarily a project that goes exactly as expected, yielding results identical to those that were predicted.
- Scrum controls the process of software development to guide work toward the most valuable outcome possible.
Kanban ⌘
- WIP
- Visibility
Conection with the above ⌘
| Lean | Agile | Scrum | Kanban |
|---|---|---|---|
| 消除浪费 | 工作的软件 高于 详尽的文档 | All | WIP限制 |
| 增强学习 | 个体和互动 高于 流程和工具 | Restrospective | |
| 尽量延迟决定 | 响应变化 高于 跟进计划 | backlogs设计,队员决定 | |
| 尽快发布 | 段迭代 | 3周Sprint | WIP Limits |
| 下放权力 | 自我团队 | 自我团队 | |
| 嵌入质量 | 客户合作 高于 合同谈判 | 会议 | |
| 全局优化 | Interdiciplinary team |
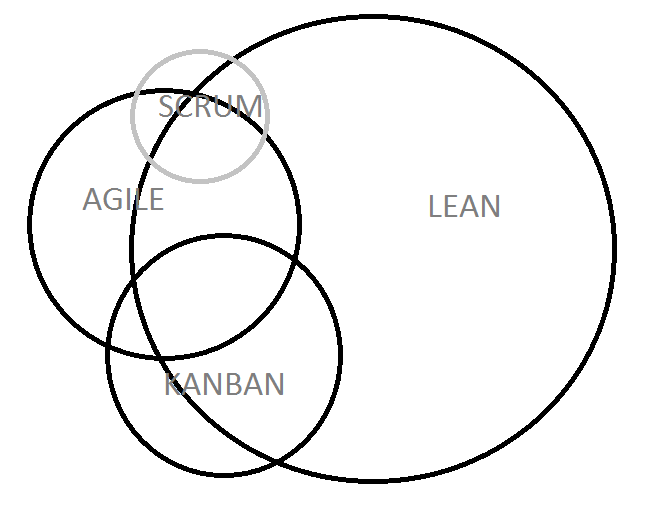
SCRUM-LEAN-KANBAN overlap ⌘
Scrum ⌘
Scrum ⌘
- Scrum是一种Agile的方法
Kanban ⌘
- Limit WIP
| Planned | Doing [Limit 5] | Finished - not tested [Limit 3] | Done |
|---|---|---|---|
| Story 1 | Story 3 | Story ... | 。。。 |
| Story 2 | Story 4 | ||
| .... | Story 5 | ||
| Story 6 | |||
| Story 7 |
Scrum ⌘
Scrum原词来自橄榄球中的“带球过人”。在橄榄球比赛的每次冲刺前,都有一个计划安排的过程
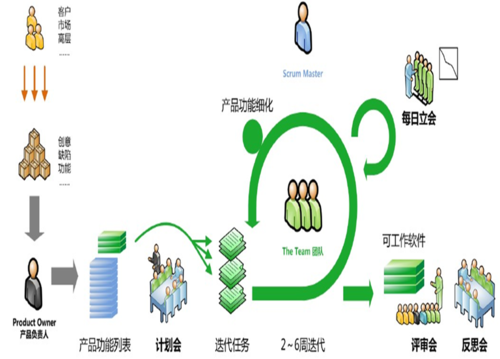
Scrum过程 ⌘
This image should be change (may have copyright issue + Daily meeting looks too official (should be circle
Scrum被谁采用 ⌘
- 百度
- IBM
- 微软
- 谷歌
- 飞利浦
- 西门子
- 诺基亚
- 英国广播公司
- 美国第一资本投资国际集团
- Nagra Vision
- Lockheed Martin
Scrum被运用的领域 ⌘
- 软件
- 网络交换路由设备
- 车开发 http://wikispeed.org/join-the-team/the-wikispeed-process/
Scrum 结构框架 ⌘
- 角色
- 产品负责人 (Product Owner, PO, 产品所有者)
- ScrumMaster (Scrum大师)
- 团队 (The Team)
- 会议
- 迭代计划 (Scrum Planning)
- 迭代验收 (评审会, Evaluation, Presentation)
- 迭代回顾 (反思会, Retrospective, Review)
- 每天召开的 scrum 会议 (每日立会, Daily Scrum, Scrum)
- 产出
- 产品backlog (产品待开发项,Product Backlog)
- 迭代backlog (迭代待开发项, Sprint Backlog)
- 进度曲线图 (燃尽图,Burn-down Chart)
Pigs and Chickens ⌘
- The people who fill the three Scrum roles are those who have committed to the project (Pigs)
- Others might be interested in the project, but they aren’t on the hook (Chickens)
Product owner (1h) ⌘
Product Owner ⌘
- Responsible for representing the interests of everyone with a stake in the project and its resulting system
- Achieves initial and ongoing funding for the project by creating:
- project’s initial overall requirements
- return on investment (ROI) objectives
- release plans
- The list of requirements is called the Product Backlog
- The most valuable functionality is produced first
- Prioritize the Product Backlog to queue up the most valuable requirements for the next iteration
The customer representative ⌘
- Ideally if PO is a curstomer itself
- If it is not possible, PO should be able to make decision on behalf of the customer without delay
Product Owner Responsibilities ⌘
An extract from http://www.scrum.org/storage/scrumguides/Scrum_Guide.pdf
- The PO is responsible for maximizing the value of the product and the work of the Development Team
- The PO is the sole person responsible for managing the Product Backlog (PB)
- Product Backlog management includes:
- Clearly expressing PB items (PBI);
- Ordering the items in the PB to best achieve goals and missions;
- Ensuring the value of the work the Development Team performs;
- Ensuring that the PB is visible, transparent, and clear to all, and shows what the Scrum Team will work on next;
- Ensuring the Development Team understands items in the Product Backlog to the level needed
- The PO may do the above work, or have the Development Team do it
- However, the PO remains accountable.
- The PO is one person, not a committee
- The entire organization must respect his or her decisions.
- The PO’s decisions are visible in the content and ordering of the PB
- No one is allowed to tell the Development Team to work from a different set of requirements, and the Development Team isn't allowed to act on what anyone else says
Prioritizing product requirements ⌘
- The lower the priority the less details are needed
- Some can be extremely vague e.g. Users can see related content (not defining what related content is or where a user will see it)
- Some authors recommend 20/30/50 rule, where
- 20% of stories are concrete and ready to roll
- 30% are epics which will be split out into smaller fine grained ones
- The last 50% are themes, vague ideas about long term product direction and people should not put much effort as they almost always change.
Backlog Prioritization Factors ⌘
- Business Value
- Time Value
- Dependency Constraint
- Technical Constraint
- Political Constraint
- Technological Development
Acceptance criteria DoD ⌘
- Product is complete
- Product prototpye is tested by testers
- Product can by used by the end user or integrated with another product
- Automated standard tests passed
- Acceptance tests passed
- Demonstrated functionality to Product Owner— received interim “Thumbs Up”
Negotiating sprint contents ⌘
- Split Epics into Stories
- Create Scenarios
- Add technical Stories
- Estimate (Estimation (Planning) Poker)
Initial Backlog Planning Meeting ⌘=
- Happens before the project starts
- PO + Stakeholders (customers, sponsors, etc..)
- Activities:
- Define scope of the project
- Write a couple of epics
- Chose Epics to go into first sprint
- Write a couple user stories
- Decide on the team(s) size
Backlog Grooming Meetings ⌘
- Can happen anytime
- PO + Stakeholders (customers, sponsors, etc..)
- Activities:
- Write user stories, epics, etc...
- Break down user stories that are too big (epics)
- Improve user stories that are poorly written
- Estimate backlog items
- Add acceptance criteria
- Remove outdated stories
- Agree on priority
Group exercise to produce customer requirements and write stories based on the requirements ⌘
- Write a simple product backlog using wiki (TODO: shall we set up wiki with ALTRAN logo?)
The sprint (3h) ⌘
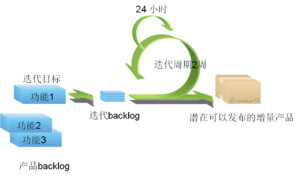
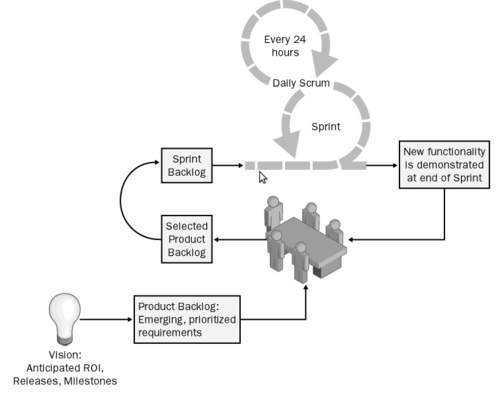
Scrum Process ⌘
Sprint backlog ⌘
- User stories
- Business value
- How to test it (acceptance criteria)
- Different schools about complexity
- Abstract size (0,1,2,3,5,8)
- Number of IDEAL days - A day in life of developer where he has everything he needs to complete the job with no disturbance.
- Planning poker
- Splitting User stories into task
- Task duration from 1 hour up to 1 day. If its gets longer, it is advisable to break it further.
Sprint planning: what to do ⌘
- Estimating and Planning (4+1)
- Define clear goals
- Everyone (not only the person who are going to develop it) MUST understand the task
- Everyone can contribute their way they see is the best
- Daily Scrums (15min every day)
- Demonstration (1h)
- Retrospection – post-mortem (1h)
Sprint planning how to do it ⌘
Planning Poker⌘
- Everyone selects complexity from Planning Poker Card
- Two extreme people explain why they thought this way
- Discussion
- Optional re-vote
- You can play poker for estimated time and estimated business value
Precision vs Accuracy ⌘
- Precise but not accurate PI number: 3.12134352343435
- Accurate but not precise number PI number: 3.14
- Try to be accurate not precise
- Precision gives false confidence about estimation
What happens during a sprint ⌘
SCRUM WALL ⌘
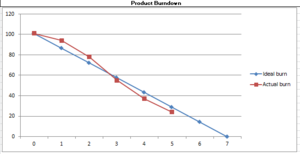
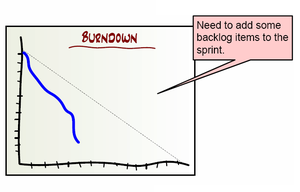
Product Burn-down Chart ⌘
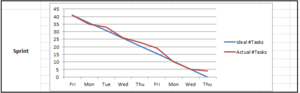
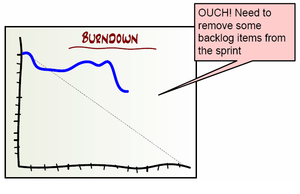
Sprint Burn-down Chart ⌘
Tools ⌘
Post-it vs tools ⌘
- Tools can confine your choices
- Post-its are simple and always visible
- Tools are recommended when you work with an outsourced teams’ members
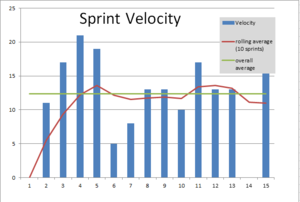
Iteration Duration and Team Velocity ⌘
- Do not change the duration of an iteration!
- What if we discovered new tasks to do in order to complete user story?
- Measurement – hours or finished tasks
- What does it mean done
- Overtime
- Adjusting next iteration
Group exercise to plan a sprint ⌘
Scrum Master (3h) ⌘
Scrum Master and Scrum Implementation ⌘
- Responsible for the Scrum process
- Teaching Scrum to everyone involved in the project
- Implementing Scrum so that it fits within an organization’s culture and still delivers the expected benefits
- Ensuring that everyone follows Scrum rules and practices
- Manager drives the team vs Scrum Master serves the team
- Scrum Master is a facilitator
Maintaining documentation ⌘
Daily Scrums (Stand up meeting)⌘
- The questions must be asked:
- What have I done since the last Daily Scrum?
- What am I going to do between now and the next Daily Scrum?
- What is preventing me from doing my work?
- People MUST stand
- Up to 15 min regardless of the team size
- Everyone invited, only pigs are talking
When to pair program ⌘
- Possibility of being stuck is high
- When two skillset is required (e.g. integration of two system/techonologies)
- When skillet is not even (mini-training) - arguable
Group exercise to implement Scrum ⌘
Finishing a sprint (3h) ⌘
Scrum review meeting ⌘
- PO
- Customer representative
- The Team
- Scrum Muster
- Other stakeholders
- Decision
- release vs improve
产出潜在可交付的产品增量(potential shippable product incremental - PSPI
- is testable by the end user
- an be release to the public
- safety certification can or cannot be included depends on the probability of failiing the test (if you do drugs, it required, for computer screen less likely so)
Scrum retrospective meeting ⌘
- Participants: Team members, Scrum Master, (optionally PO, but it is internal team business to improve their process)
- Is previous improvement effective?
- What did we do right? (keep it)
- What should we avoid? (throw it away)
- What should we try next time? (how to improve)
Group exercise the review a sprint ⌘
....
Kanban (1h) ⌘
Factory model ⌘
- Hirerachical Structure
- Matrix Structure
Pillars of Kanban & Big Picture ⌘
Process ⌘
Concepts behind Kanban ⌘
Kanban Rules &Metrics ⌘
Flow Diagram+ technical practices ⌘
The Team ⌘
Self-organization & Interdisciplinary ⌘
Benefit the "right" team work ⌘
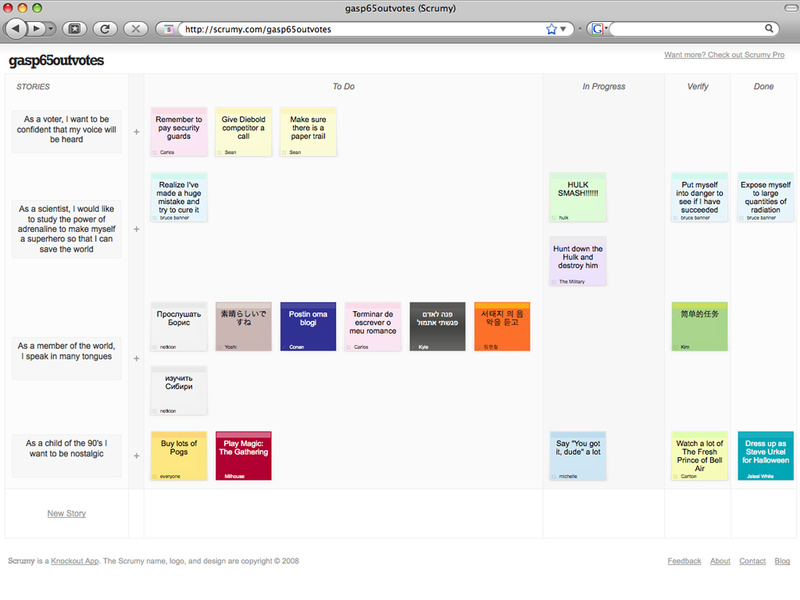
Kanban Board ⌘
How to visualize process? & How to create Kanban Board? ⌘
What are and how to introduce WIP limits? ⌘
What are and how to introduce Classes of Service? ⌘
Customer Engagement ⌘
The most common waste ⌘
Value Stream ⌘
Product Discovery Methods and Tools (1h) ⌘
- Golden Circle
- Impact mapping
- Design Thinking
- User story mapping
Golden Circle 1 ⌘
- What does your company do?
- How do they do it?
- Why your company what they do?
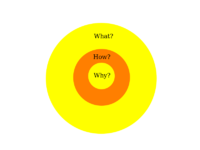
Golden Circle 2 ⌘
- Traditional
- What
- How
- A bit better way
- Why
- How
- What
 More: http://www.slideshare.net/ohmgrrl/sinekexpand1/35-Images_Sun_slide_1_jenny
More: http://www.slideshare.net/ohmgrrl/sinekexpand1/35-Images_Sun_slide_1_jenny
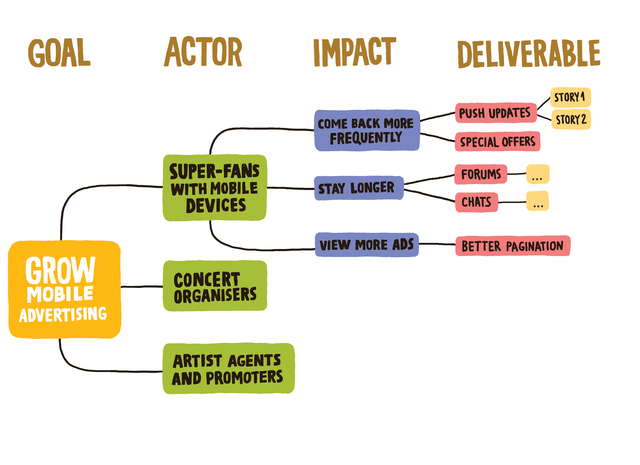
Impact Mapping ⌘
From: https://www.impactmapping.org/drawing.html