Other Technologies
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Web Services Basics For Non-programmers
- author
- Pete George (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
Day Two Schedule ⌘
- WSDL
- Handling Binary Content
- RESTfull Web Services
- Other Technologies
- Conclusion
Other Technologies ⌘
- Learning Objectives
- To be aware of other technologies associated with Web services:
-Cloud Computing
-Enterprise Service Bus
-Integration Platforms
-iPaaS
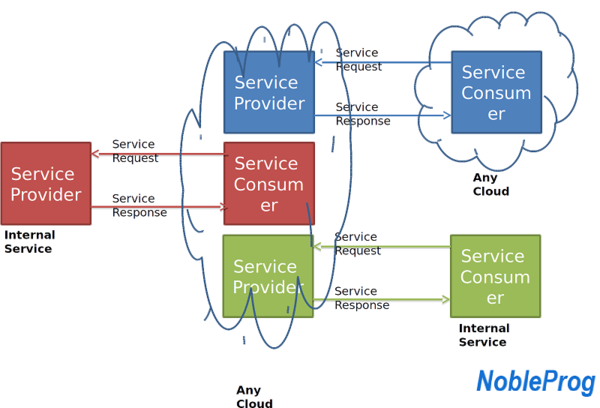
Cloud Computing ⌘
- Software and hardware resources provided via the Internet
- Web services or Web API’s used as connections to Cloud
- Less distinction between internal and external services
- No cost or fee-for-use Cloud services available
SOA with Cloud Computing ⌘
Types of Cloud ⌘
- Public
- Community
- Private
- Virtual Private
Categories of Cloud Providers ⌘
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-Provides physical and virtual resources to build cloud
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-Provides platform to build applications
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
-“on-demand software”
-Provides complete applications
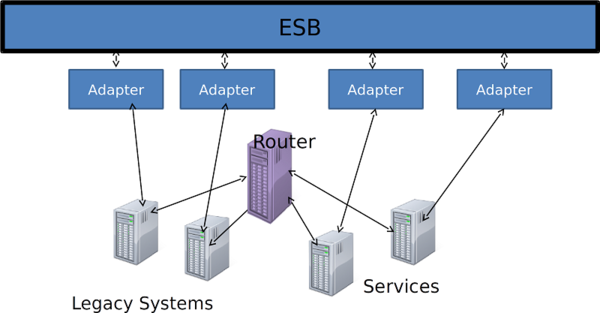
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) ⌘
- Important in distributed systems to propagate data among internal systems promptly
- ESB is a solution to help manage this
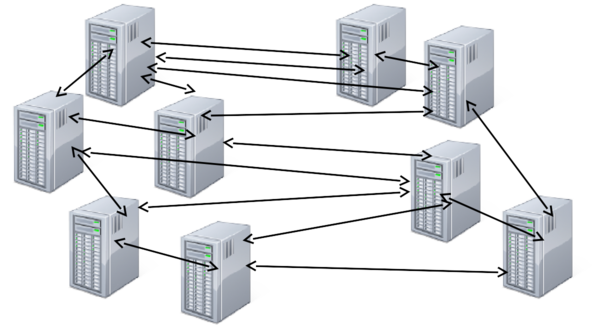
Multiple Connections ⌘
- Complexity increases with multiple connections
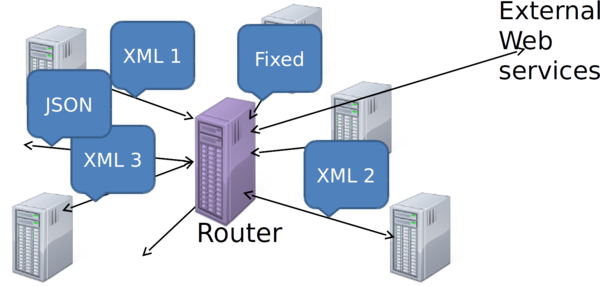
Message Router ⌘
- Message Router or Application Router
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) ⌘
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) ⌘
- Manages transfer of data among different types of software
- Controls routing as a router
- Monitors and logs message routing
- Enable services to easily plug into system
ESB Adaptors ⌘
- Enable transformation of protocols and messages
- Ensure standard vocabulary used throughout organisation
Integration Platforms ⌘
- Software which integrates different applications and services
- Different Approaches
-Built from components
-Purchased pre-built product ready for installation
-Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
Integration Platforms Components ⌘
- Message bus
- Adapters to transform messages from and to protocols
- Transformation engine to transform messages or files
- Metadata repository for storing information
- Process Orchestration Engine for orchestration design and execution
- Technical dashboard for tracking
- Scheduler for scheduling orchestrations
- Batch engine for controlling large file transfers, batch jobs, execution of external scripts and other non-messaging based tasks
Integration Platform as a Service ⌘
- “Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is a suite of cloud services enabling development, execution
and governance of integration flows connecting any combination of on premises and cloud-based processes,
services, applications and data within individual or across multiple organizations.”
(Gartner)
Integration Platform as a Service ⌘
- A Platform:
-That allows users to connect applications across multiple web services and organizations
-Deploy integrations without having to install new hardware, software or create custom code.
- Provide interoperability and automation between cloud platforms, using APIs
iPaaS Drivers ⌘
- Personal Cloud – The personal cloud will gradually replace the PC as the location where individuals keep their personal content, access their services and personal preferences and center their digital lives.
- Internet of Things – The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that describes how the Internet will expand as physical items such as consumer devices and physical assets are connected to the Internet.
- Strategic Big Data – Big Data is moving from a focus on individual projects to an influence on enterprises’ strategic information architecture. This realization is leading organizations to abandon the concept of a single enterprise data warehouse containing all information needed for decisions. Instead they are moving towards multiple systems, including content management, data warehouses, data marts and specialized file systems tied together with data services and metadata, which will become the “logical” enterprise data warehouse.
- APIs, web and mobile apps, cloud platforms, and other advances in technology are causing enormous amounts of data to be generated, shared and stored in data silos across many different types of applications and organizations. Data is becoming increasingly disconnected between web and cloud apps.
(Gartner)