Microsoft SQL Server Administration ENG
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Microsoft SQL Server Administration
- author
- Jarosław Sołoducha
</slideshow>
Agenda ⌘
- SQL Server Services, Versions, Editions
- Management Studio
- T-SQL basic overview
- Databases overview
- Stored Procedures, Views, Triggers
- Indexes
- Transaction Log
- Recovery Models
Agenda ⌘
- Backups and Restore
- Working with DB ( copy, shrink...)
- Jobs & Maintenance Plans
- Security
- Upgrade
- Monitoring
Basic information about Databases⌘
- MS Access
- Databases Client/Server
- Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS):
- DB2
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL
What is a SQL Server ?⌘
- Relational Database Management System
The RDBMS of SQL Server is responsible for:
- Maintaining the relationships among data in a database.
- Ensuring that data is stored correctly and that the rules defining the relationships among data are not violated.
- Recovering all data to a point of known consistency, in the event of a system failure.
SQL Server Editions⌘
- Enterprise
- Standard
- Web
- Express
- Developer
SQL Server Versions ⌘
- Select @@version
- SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('productversion'), SERVERPROPERTY ('productlevel')
- Configuration Manager
https://sqlserverbuilds.blogspot.com/
SQL Server Tools⌘
- SQL Server Management Studio
- Business Intelligence Development Studio
- SQL Server Agent
- SQL Server Profiler
- Database Tuning Advisor
Services in SQL Server ⌘
- Database Services
- Analysis Services
- Reporting Services
- Integration Services
Database Services ⌘
Database Services includes:
- Data files
- Replication
- Full-Text search
Analysis Services - SSAS ⌘
Also known as DataWarehouse
Provides online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining functionality for business intelligence applications.
- Analytical data processing
- Decision support
- Data centralization
- Archiving
Reporting Services - SSRS ⌘
Manages, executes, renders, schedules, and delivers reports.
- Report Manager
- Report Builder
- Visual Studio
- PowerBI
Intergration Services - SSIS ⌘
- Provides management support for SSIS package storage and execution.
- Integration Services is a platform for building high performance data integration solutions,
including packages that provide extract, transform, and load (ETL) processing for data warehousing
SQL Server Service accounts ⌘
- "NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE"
- This user account is created in your server where SQL Server is installed
- this account does not have access to network resources.
- "NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE"
- This is a builtin windows account that is available for configuring services in windows.
- This has permissions to access resources in the network under the computer account.w
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc281953%28v=sql.120%29.aspx
SQL Server Service accounts part.II ⌘
- "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
- This is a builtin windows account that is available for configuring services in windows.
- This is a highly privileged account that has access to all resources in the server with administrator rights.
- "Domain Account"
- This account is a part of your domain that has access to network resources for which it is intended to have permission for.
- It is always advised to run SQL Server and related services under a domain account with minimum privilege need to run SQL Server and its related services.
SQL Server Service accounts part.III ⌘
Group Managed Service Accounts
- Managed Service Accounts are not like normal Active Directory user accounts, additionally:
- they do not permit interactive login,
- are internally associated with the specified computer account,
- use a similar mechanism to Active Directory computer accounts for password management.
https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/5340/using-group-managed-service-accounts-with-sql-server/
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/markweberblog/2016/05/25/group-managed-service-accounts-gmsa-and-sql-server-2016/
Sql Server Network Protocols ⌘
- Microsoft SQL Server can handle requests from several protocols at the same time.
- Protocol configuration - SQL Server Config Manager
Protocols in SQL Server:
- Shared Memory
- TCP/IP
- Named Pipes
- If you have to enable a protocol, or make any other changes in the SQL Server Configuration Manger, it is necessary to restart the SQL instance.
Data Manipulation Language (DML)⌘
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
*short exercise
Data definition language (DDL)⌘
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DROP
*short exercise
System Databases ⌘
- master
- model
- msdb
- tempdb
- distribution*
- resource*
Master ⌘
- the most important database
- first database which is being started
- SQL Server configuration, information about:
- system objects
- logins
- location of individual SQL files
- user databases
Model ⌘
"Template" database fo all other user databases
Msdb ⌘
- Database used by SQL Server Agent
- Contains information about:
- jobs
- backups history
- SSIS packages
Tempdb ⌘
- Temporary database
- It is created from the scratch after each service restart
- Contains temporary objects:
- tabels
- cursors
- various objects created internally by SQL
Tempdb ⌘
- Separate fast disk - SSD
- Create as many files as there are processors, but not more than 8
Distribution* ⌘
- Created if there is replication on the Server
- Contains metadata and replication historical data
Resource* ⌘
- This is a hidden database which can be seen only via DAC connection
when SQL is running in single user mode. - Contains only the definition of system objects.
- No data specific to instance is stored.
- Database ID for this database is always 32767
Database creation
SQL files and their locations⌘
- .mdf
- .ndf
- .ldf
- FileGroups
- Physical and logical names of files
Initial size and autogrowth ⌘
- big or small ?
- Model database
- Autogrowth
Table partitioning ⌘
- Available only in Enterprise and Developer editions of SQL Server (and evaluation versions)
- Increased speed of data access
- Easier data management
- Most often used to divide data by "age"
- Required permissions: sysadmin, db_owner and db_ddladmin.
Table design⌘
- Columns and their attributes
- Data types
- - Text (char, varchar, nchar, ntext, nvarchar)
- - Numeric (int, smallint, bigint, tinyint, float, real, decimal, numeric)
- - Dates and times (datetime, smalldatetime)
- - Binary (binary, varbinary)
- - Currencies (money, smallmoney)
- - Special (text, image, xml, bit)
*demo
Indexes ⌘
- Index in the database is a type of structure closely related to the table or view,
which helps significantly speed up the access to data. - The index contains one or several connected columns of the table or view.
- The keys in the index are stored in a structure called a B-tree
Indexes ⌘
- Clustered
- Non-Clustered
The most important for the index's effectiveness are:
- - high index selectivity
- - "up to date" statistics
- - low level of fragmentation
Indexes - Primary Key ⌘
- Primary key is a single field or combination of fields that uniquely defines a record.
- None of the fields that are part of the primary key can contain a null value.
- A table can have only one primary key.
Indexes - Foreign Key ⌘
- A foreign key is a way to enforce referential integrity within your SQL Server database.
- A foreign key means that values in one table must also appear in another table.
- The referenced table is called the parent table while the table with the foreign key
is called the child table.
The foreign key in the child table will generally reference a primary key in the parent table.
Clustered Indexes ⌘
- One clustered index on the table
- Most often created on a column with high 'selectivity'
- Primary key - clustered index
Non-Clustered Indexes ⌘
- Up to 999 indexes nonclustered on the table
- Can be based on clustered indexes.
- Pointers to data
*video
REBUILD vs. REORGANIZE ⌘
- REBUILD deletes and creates indexes from scratch,
- REORGANIZE only sorts pages, doesn't delete them,
- both REBUILD and REORGANZIE reduce fragmentation
(AVG_FRAGMENTATION_IN_PERCENT column in sys.dm_db_index_physical_stat view)
Fragmentation:
- 0 - 10% - nothing
- 11 - 30% - REORGANIZE
- 31 - 100% - REBUILD
REBUILD vs. REORGANIZE- skrypt ⌘
SELECT DB_NAME(PS.database_id) AS dbName,
S.name AS SchemaName,
O.name AS TableName,
b.name,
ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL) AS ps
INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS b ON ps.OBJECT_ID = b.OBJECT_ID AND ps.index_id = b.index_id
INNER JOIN sys.objects O ON PS.object_id = O.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.schemas S ON S.schema_id = O.schema_id
WHERE ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent >= 20 -- Indexes having Fragmentation >=20
AND PS.index_type_desc IN ('CLUSTERED INDEX','NONCLUSTERED INDEX') -- Only get clustered and nonclustered indexes
AND b.is_hypothetical = 0 -- Only real indexes
AND O.type_desc = 'USER_TABLE' -- Restrict to user tables
AND PS.page_count > 8 --- ignore tables less than 64K
ORDER BY ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent,name DESC
"Developing" on SQL Server side ⌘
- Stored procedures
- Views
- Triggers
- Functions
Procedures ⌘
- Accept input parameters and return multiple values in the form of output parameters to the calling procedure or batch.
- Contain programming statements that perform operations in the database, including calling other procedures.
- Return a status value to a calling procedure or batch to indicate success or failure (and the reason for failure).
- Access rights needed to create stored procedures: sysadmin ; db_owner ; db_ddladmin
*demo
Views ⌘
- Virtual table which content (columns and rows) is defined by a query.
- Security mechanism by allowing users to access data through the view,
without granting the users permissions to directly access the underlying base tables - Can have indexes defined.
*demo
Triggers ⌘
Trigger is a special kind of stored procedure that executes automatically
when a user attempts the specified data-modification statement on the specified table
Types of Triggers:
- FOR
- AFTER
- INSTEAD OF
*demo
Functions ⌘
- Function is a database object in SQL Server.
- Basically, it is a set of SQL statements that accept only input parameters,
perform actions and return the result. - Function can return an only single value or a table.
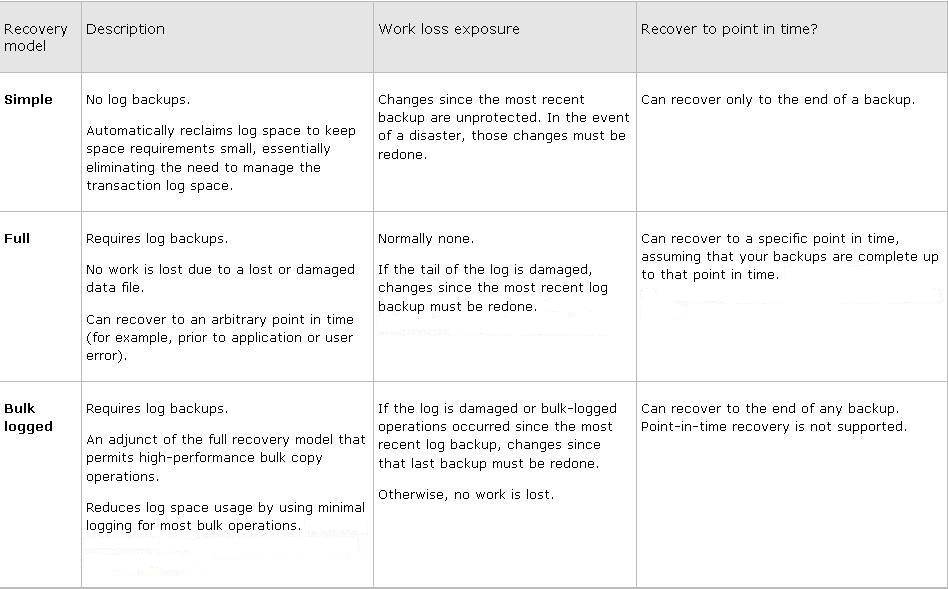
Recovery Models ⌘
- Simple
- Full
- Bulk logged
Recovery Models ⌘
Backups ⌘
- Full
- Differential
- Transaction log
Full Database Backup ⌘
BACKUP DATABASE master TO DISK = 'D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\Mssql\Backup\master.bak'
- A full database backup backs up the whole database ( data, tables, procedures, views ..)
This includes part of the transaction log so that the full database
can be recovered after a full database backup is restored.
- Full database backups represent the database at the time the backup finished.
- First starting "point" in recovery
Differential Database Backup ⌘=
BACKUP DATABASE Northwind TO disk='D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\Mssql\Backup\Northwind_diff.BAK' WITH DIFFERENTIAL
- A differential backup is a type of data backup method that copies all of the files that have changed since the last full backup was performed.
- Differential backup includes any data that has been created, updated or altered in any way and does not copy all of the data every time.
Transaction Log Backup ⌘=
BACKUP LOG Northwind TO disk='D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\Mssql\Backup\Northwind_log.TRN'
- The transaction log backup allows to restore a database to a particular point-in-time before the failure has occurred.
- It is incremental, meaning that in order to restore a database to a certain point-in-time,
all transaction log records are required to replay database changes up to that particular point-in-time.
Database backup's strategies ⌘
- Full Backup
- Full + Transaction Log backup
- Full + Differential + Transaction Log backup
Full Backup strategy⌘
- Used for small or rarely modified databases.
- Usually performed daily
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
|---|---|
|
Low number of backups |
Risk of data loss since the last full backup |
Full + Transaction Log backup strategy ⌘
It is recommended for ( medium and ) frequently modified databases.
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
|---|---|
|
The ability to restore data from any point before failure. |
Frequent (at least daily) full backup. |
Full + Differential + Transaction Log backup strategy ⌘
It is recommended for big databases.
| Advantages: | Disadvantages: |
|---|---|
|
Shorter backup times |
A more difficult database restore process.
|
Full + Differential + Transaction Log backup strategy ⌘
- comparison of backup strategies
exercises:
- backups
- restore
*autogrowth demo
Copying Databases ⌘
- deatach , copy files, attach files
- backup and restore
- wizard - not recommended
Problem with users SID when DB is being migrated to another SQL Server or instance
*exercise
Shrinking ⌘
Fisrt of all – DON’T DO IT !!!!
- Shrinking should be a rare operation and should not be part of any regular maintenance you perform.
- Shrinking of data files should be performed even more rarely, if at all.
- You should NEVER, NEVER have auto-shrink enabled
- DBCC SHRINKDATABASE vs. DBCC SHRINKFILE
*exercise
Automation in SQL Server⌘
- SQL Agent
- SQL jobs: create, manage, schedule
- MSDB
Maintenance Plans ⌘
- Sysadmin rights needed
- Workflow of Tasks
- Checking database integrity DBCC CHECKDB
- Statistics
- Index maintenance - Rebuild vs Reorganize
*exercise
Security basics⌘
- Creating accounts:
- Active Directory
- SQL Account
- Schemas
- SA account
- Server roles
- Database Roles
Server roles ⌘
- bulkadmin
- dbcreator
- diskadmin
- processadmin
- public
- securityadmin
- serveradmin
- setupadmin
- sysadmin
Database roles ⌘
- db_accessadmin
- db_backupoperator
- db_datareader
- db_datawriter
- db_denydatareader
- db_denydatawriter
- db_owner
- db_securityadmin
- public
Schemas ⌘
- Objects that contain objects of other types (e.g. tables, procedures)
- Simplification of administrative tasks
- Schema owner
- Ownership transfer
*demo
Monitoring SQL Server activity ⌘
- Activity Monitor
- DMVs
- Performance counters + PAL
- Extended events
- Performance Dashboard Reports
- SQL Server Profiler
- Data Collector
http://www.sqlcoffee.com/SQLServer2008_0009.htm
Upgrade ⌘
- InPlace vs Migration
- Service-Pack
- Cluster
TEST :) ⌘
Best Practices ⌘
- Separate disks for user database files, TempDB, System DB’s
- Regular Backups
- Restricted access rights
- Regular monitoring of DB’s growth
- Test environment
- Follow "highly skilled" specialists
- Good documentation
Links ⌘
- www.youtube.com
- www.sqlservercentral.com
- www.udemy.com
Survey and Certificates ⌘
The End ⌘
THANK YOU ! & GOOD LUCK !