Enterprise Integration
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="。" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Enterprise Integration
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (bs@NobleProg.co.uk)
</slideshow>
What is EI 。
- Enterprise Integration is a technical field of Enterprise Architecture
- Focused on systems and applications interconnection, EDI, Distributed Computing
"EI aims to connect and combines people, processes, systems, and technologies to ensure that the right people and the right processes have the right information and the right resources at the right time" Brosey (2001)
EI versus Application Development 。
- Overwhelming spending in IT is on EI rather than application development (Gartner TODO: find exact quote)
- Building or buying an application is actually much easier
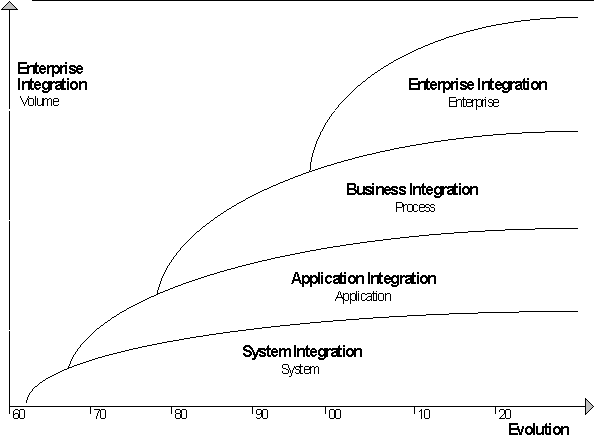
Enterprise, System, Application Integration。
EI needs。
- Identify the right information
- Provide the right information at the right place
- Up-date the information in real time to reflect the actual state of the enterprise operation
- Co-ordinate business processes (BPMS)
- Organize and adapt the enterprise
Enterprise Integration Act of 2002。
- The Public Law 107-277
- Authorizes the National Institute of Standards and Technology to work with major manufacturing industries on an initiative of standards development and implementation for electronic enterprise integration, etc.
Enterprise Application Integration。
- EAI is "The use of software and computer systems architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications" (Wikipedia)
- EAI is "Unrestricted sharing of data and business processes among any connected application or data sources in the enterprise." (Gartner Group)
Enterprise Integration Patterns。
Mediation (intra-communication)
- EAI system acts as a broker between multiple applications
- When an event occurs in an application an EAI system is notified
- The EAI propagates the changes to other applications.
Federation (inter-communication)
- EAI system acts as the overarching facade across multiple applications
- All event calls from the 'outside world' to any of the applications are front-ended by the EAI system
- The EAI system is configured to expose only the relevant information and interfaces of the underlying applications to the outside world, and performs all interactions with the underlying applications on behalf of the requester.
Both patterns can and often are used concurrently
Other Aspects of EAI 。
- Topology: bus vs hub
- Application connectivity (message formats like SOAP, SMTP, AMF and adapters)
- Transactions (two-phase commit vs compensation)
- Queuing (FIFO, LIFO, broadcasting)