Enterprise Architecture in an Enterprise
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Enterprise Architecture in an Enterprise
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (bs@NobleProg.co.uk)
</slideshow>
Enterprise Architecture in an Enterprise⌘
- Strategic Management, Strategic Planning
- OMG Business Motivation Model
- Balanced Scorecards
- Strategy Execution (EFQM)
- Quality Management
- Six Sigma
- TQM
- ISO 9001
- IT Governance: COBIT
- IT Service Delivery and Support (ITIL)
- IT Implementation (CMM and CMMI)
Area of Management relevant to EA⌘
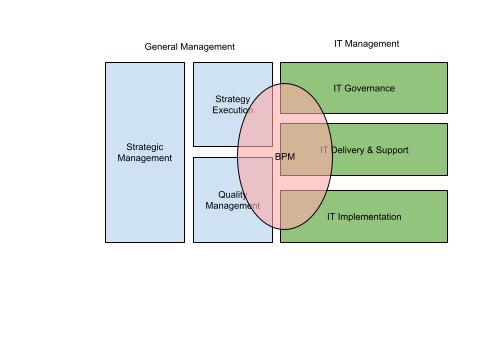
Strategic Management⌘
- Business Motivation Model (BMM)
- Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Balanced Scorecard Example
| Internal Business Process Metrics | |||||||||
| Internal Objective Type | Measures | Targets | Supporting Initiatives | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation | Percentage of sales from new products | 5% of revenues will come from new products A and B. | New markets team will drive sales of new products through indirect channel. | 1% | 2% | 4% | 5% | 5% | Target achieved |
| Operations | Product quality | Defects will be reduced from 3 in every 1,000 to 1 in every 1,000 by June. | |||||||
| Post-sales service | Warranty and repair costs | Warranty costs will be reduced by 50% by the end of the year. | |||||||
Strategy Execution⌘
EFQM - European Foundation for Quality Management Excellence Model (2010)
- Introduced in 1992 as the framework for assessing applications for the European Quality Award
- Inspired by the Deming Prize in Japan and Malcolm Baldrige Model in the USA
TODO Describe EFQM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U4K2_QEMP2s
Quality Management ⌘
Six Sigma
Relation to Enterprise Architecture
- Architecture allows to easier
TODO: Describe Six Sigma (OCEB + SigSigma slides)
- Total Quality Management
IT Governance: COBIT ⌘
- Control Objectives for Information and related Technology
- Standard for IT governance
- Published in 1996 by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association)
- The current version COBIT 5 published in 2012
Its mission is: * to research, * develop, * publish and * promote an authoritative, up-to-date, international set of generally accepted information technology control objectives for: * day-to-day use by business managers, * IT professionals and * assurance professionals.”
IT Governance: COBIT ⌘
- Provides good practices across a domain and process framework
- Links business goals to IT goals, providing metrics and maturity models to measure their achievemen
- Its process model subdivides IT into four domains:
- Plan and Organize
- Acquire and Implement
- Deliver and Support
- Monitor and Evaluate
- COBIT responsibility areas: plan, build, run and monitor
Aligned and harmonized with other, more detailed, IT standards and good practices such as COSO, ITIL, ISO 27000, CMMI, TOGAF and PMBOK
- Provides Maturity Model (similar to CMMI)
- COBIT focuses on how to organize IT functions
- Enterprise Architecture concentrates on the primary business and IT organization
IT Service Delivery and Support: ITIL⌘
- IT Infrastructure Library
- Focuses on IT asses management
- Originally developed by the UK Office of Government Commerce (OGC) for the UK central government
- Contains best practices for IT service management
- De facto standard for IT service management
- IT Service Management Forum (itSMF) - forum for IT Service Management professionals
- Provides guidance on the design and implementation of the various processes
IT Service Delivery and Support: ITIL⌘
ITIL processes
- Service Delivery
- service-level management
- availability management
- financial management for IT services
- IT service contingency management
- capacity management
- Service Support
- problem management
- incident management
- service desk
- change management
- release management
- configuration management
IT Service Delivery and Support: ITIL⌘
ITIL and COBIT
- Complementary to COBIT
- COBIT objectives can be implemented through ITIL
- COBIT control objectives tell what to do - ITIL explains how to do it (best-practice)
ITIL and EA
- ITIL deals with the IT Assents Management
- EA, especially the relation of applications to infrastructure helps better assents management
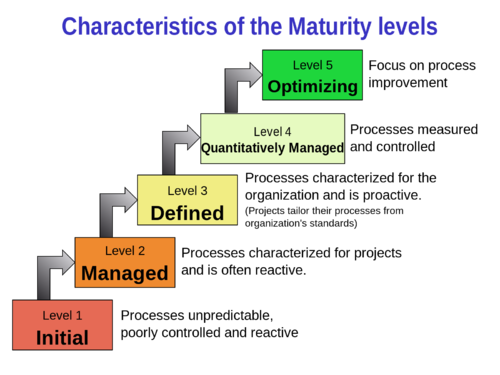
IT Implementation: CMMI ⌘
- Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
- Process improvement approach
- Can apply to a project, a division, or an entire organization
- Current version 1.3 released in November 2010
- CMMI is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office by Carnegie Mellon University.
CMMI:
- helps integrate separate organizational functions
- set process improvement goals and priorities
- provide a point of reference for appraising current processes
IT Implementation: CMMI ⌘
- CMMI supersedes CMM
TODO:
CMMI is abstract, therefore a lot of other Maturity Models use it as a foundation for more specific frameworks (see COBIT and OMG BPMM)
Relation to EA
- EA provides constraints and guidelines for individual software projects
- CMMI Level 3 almost requires EA in place (organization-wide standards and guidelines)
ISO 9001 ⌘
- Standards related to Quality Management Systems
- Published by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
- One of the most widely used management tools in the world (Over a million organizations worldwide)
- Designed to help organizations ensure that they meet the needs of customers and other stakeholders
- Deals with
- the fundamentals of quality management systems and
- the requirements that organizations wishing to meet the standard have to fulfil
EA and ISO 9001
- EA facilitate ISO 9001 conformance of process identification and documentation
- Quality Management say what needs to be designed, documented, controlled, measured and improved
- EA determines how the processes and resourced are organized and implemented