Enterprise Architecture Methods and Frameworks
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Enterprise Architecture Methods and Frameworks
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (bs@NobleProg.co.uk)
</slideshow>
Framework and Methodologies ⌘
- Architecture Frameworks structure architecture description
- It can prescribe views and viewpoints
- Can suggest or enforce specific language
- Architecture Methodology is a structure collection of techniques and processes
- Methodologies usually are more restrictive than frameworks
- They specify processes for creating and maintaining an EA
RUP ⌘
- IBM RUP although heavy, is considered iterative and Agile (as oppose to waterfall)
- Enterprise Unified Process extends RUP in the area of system support and system retirement
- It is still mostly focus on Software Development, Rational Software Architect supports EA modelling extensions
UN/CEFACT ⌘
- UN/CEFACT's Modeling Methodology (aka UMM)
- Developed by UN/CEFACT - United Nations Center for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business
- Capture business requirements of inter-organizational business processes
- The UMM model can then be used to derive deployment artifacts for the IT systems of the participating business partners
- Restricted to business operations (technology independent)
ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011 ⌘
- "ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011 addresses the creation, analysis and sustainment of architectures of systems through the use of architecture descriptions"
- "A conceptual model of architecture description is established."
- "The required contents of an architecture description are specified."
- "Architecture viewpoints, architecture frameworks and architecture description languages are introduced for codifying conventions and common practices of architecture description."
- "The required content of architecture viewpoints, architecture frameworks and architecture description languages is specified."
- http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/42010-2011.html
- Supersedes IEEE 1471
- Clearly separates Architectures and Architecture Descriptions
Definitions ⌘
- Architecting: process of conceiving, defining, expressing, documenting, communicating, certifying proper implementation of, maintaining and improving an architecture throughout a system’s life cycle
- Architecture: fundamental concepts or properties of a system in its environment embodied in its elements, relationships, and in the principles of its design and evolution
- Architecture description (abbreviation 'AD'): work product used to express an architecture
- Architecture description language (abbreviation 'ADL'): any form of expression for use in architecture descriptions
- Architecture framework: conventions, principles and practices for the description of architectures established within a specific domain of application and/or community of stakeholders
- Architecture viewpoint: work product establishing the conventions for the construction, interpretation and use of architecture views to frame specific system concerns
- Architecture view: work product expressing the architecture of a system from the perspective of specific system concerns
- Concern: interest in a system relevant to one or more of its stakeholders
- Stakeholder: individual, team, organization, or classes thereof, having an interest in a system
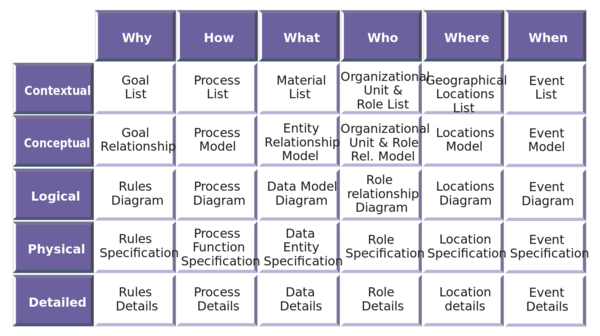
Zachman Framework ⌘
- Created by John zachman in 1987
- First comprehensive EA framework
- Limited practical applicability
- Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise
- Provides a formal and structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise
- It consists of a two dimensional classification matrix based on the intersection of six communication questions (What, Where, When, Why, Who and How) with six rows according to reification transformations
- It does not imply any specific method or process (pure framework)
UAF
- OMG standard
- derived from UPDM
TOGAF® ⌘
- Developed by The Open Group
- EA Framework + Methodology: Architecture Development Method (ADM)
- Provides a comprehensive approach for designing, planning, implementation, and governance of an enterprise information architecture
- Typically modelled at four levels:
- Business, Application,
- Data,
- Technology
- Latest Enterprise Edition release 9.1 (2011)
- TOGAF taxonomy of views is compliant with the IEEE standard
OMG MDA⌘
- Model-Driven Architecture
- Released by OMG in 2001
- Latest version released in 2003 (some frameworks where still developed as to the 2008 http://www.andromda.org)
- Idea is that the model stays the same, and the software is generated from the model using the newest technologies available
- This allows for seamless migration from a technology to new technology
- Though the standard itself is not actively developed, the idea of Model-Driven Architecture is still developing for example in case of BPMN and BPMNS (jBPM, Intalio, etc...)
SOA ⌘
see SOA materials
Military Related Frameworks ⌘
- Nato Architecture Framework
- MoDAF
- DoDAF
- UPDM
US Government Frameworks ⌘
- FEAF
- FEA
- FEAPMO
- Treasury Architecture Development Process
Other Frameworks ⌘
- RM-0ODP
- GERAM
- Nolan Norton Framework