Drools Overview
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Trebuchet MS" headingmark2="。" lang="中文版">
- title
- Drools Overview
- author
- 安博 Bernard Szlachta (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
Drools Overview Training Materials
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
About Me。⌘
- 安博 (Bernard Szlachta)
- Working with Drools/jBPM since 2007 (some projects for CERN, Philips, etc...)
- Obsessed with getting logic neat
- Wrote a couple of Rule Engines myself
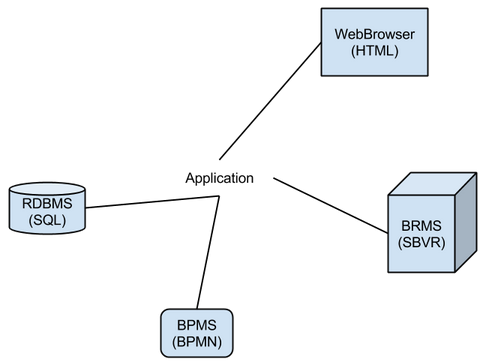
Approach to Business Analysis and Design。⌘
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AI_winter
- Data First (RDMS)关系数据库管理系统 - 1970s
- Object Orientation (OOP) 面向对象程序设计 - 1980s
- Processes First (BPMS) 业务流程管理系统 - 1990s
- Rules First (BRMS)业务规则管理系统 - first wave LISP/PROLOG - 1980 - practical use - 2000s
Data Approaches 。⌘
- First approaches to analysis focused on data first
最初,业务分析的方法关注的是“数据第一”。- This lead to people storing a lot of data but really did not use it in efficient manner
人们保存了许多数据,但是这些数据并没有很有效率地被利用。 - major problem at the time was ensuring that data is in the system rather than on paper (e.g. CIA Oracle project)
那时候重要的问题是保证数据保存在系统里,而不是在纸面上(比如CIA Oracle project)
- This lead to people storing a lot of data but really did not use it in efficient manner
OOP 。⌘
- business logic was mixed up with data
后来,业务逻辑开始和数据混合在一起(比如object constructors, etc...)
BPMs 。⌘
- Process management tools allowed analyst to create executable process models
过程管理工具允许分析师创建可执行的过程模型- first true standard came along in 2004 BPMN 1.0 (execution through translation to BPEL)
第一个真正的标准是2004年的BPMN 1.0(转译成BPEL后执行) - 2008 - BPMN2 - direct execution of BPMN file
- first true standard came along in 2004 BPMN 1.0 (execution through translation to BPEL)
BRMS 。⌘
- Though Expert system existed from 70s, they started to be used in typical commercial setup in 2000s.
虽然专家系统从70年代就已经存在,但是它们直到2000年以后,才真正应用到商业领域。 - Having rules and processes, a person can derive everything else (e.g. underlying data model, etc...)
使用规则和过程,人们可以提取出所有其它的东西(比如底层的数据模型等等),- So starting with analysing rules and processes is the easiest way
所以从分析规则和过程来起步,才是最容易的方法。
- So starting with analysing rules and processes is the easiest way
- If analysis, for example, starts with UI or datamodel, there is no way to know what the logic should be
如果分析师从用户界面或者数据模型起步,没有办法知道系统逻辑是什么
Shift towards declarative languages standards | 声明式语言标准的演化。⌘
Shift declarative languages standards。⌘
- Popular Standard languages are declarative
- SQL, HTML, BPMN populartiy reduced code needs to be written and allow non-technical people to contribute more into application development
- Rules do not have any real standards at the moment
- OMG SBVR - not used
- OMG Production Rule Representation (PRR)
- MVEL - used by few engines, but may face legal issues
- Also no leading declarative integration standard
- Declarative Open Source solution exists (Apache CAMEL, ServiceMix, etc...)
Artificial Intelligence ⌘。
Write down on your own answers to the question below:
- What is artificial intelligence? 人工智能是什么?
- What is a difference between AI method and traditional programming? 人工智能和传统的程序有什么区别?
- What are the benefits of using artificial intelligence? 人工智能有什么好处?
- Why AI isn't used everywhere? 为什么现在没有太多人用人工智能?
Artificial Intelligence ⌘。
人工智能主要分为两个部分
- Rule Engines - More Deterministic - 规则引擎 - 确定性方法
- 一样的输入一样的输出
- Machine Learning - More Probabilistic - 机器学习,统计学习-概率方法
- 一样的输入输出可能不同
Problems ML vs RE ⌘。
- What should be a pension for a specific person? 每个人的退休金应该是多少?
- Credit Card transaction is fraudulent? 信用卡交易是不是欺诈性的?
- What is the price of the insurance premium?保险的价格是多少?
- Machine Translation? 机器翻译
- What should be current price of a stock? 股票的实时价格是多少?
Write down your problems and think of the best solution?
Artificial Intelligence And Rules Engine ⌘。
- Neural Networks, Genetic Algorithms, Decision Trees, Frame Systems and Expert Systems
- Expert Systems are also known as Knowledge-based Systems and Knowledge-based Expert Systems
- Drools is a Rule Engine that uses the rule-based approach to implement an Expert System and is more correctly classified as a Production Rule System.
- 不仅仅是规则引擎,他还是Production Rule System, or Business Rules Management System (BRMS)
Rule Engines ⌘
- What is a rule?
- What is a Rule Engine?
- Why use a Rule Engine?
- Advantages of a Rule Engine
- When should you use a Rule Engine?
- When not to use a Rule Engine
- Scripting or Process Engines
- Strong and Loose Coupling
规则引擎 。
- 什么是规则?
- 什么是规则引擎?
- 为什么使用规则引擎?
- 规则引擎的优势
- 何时使用规则引擎?
- 何时不用规则引擎
- 脚本(Scripting)或过程引擎(Process Engines)
- 强耦合和弱耦合
业务规则是什么? ⌘。
“规则基于facts,而facts基于terms.”
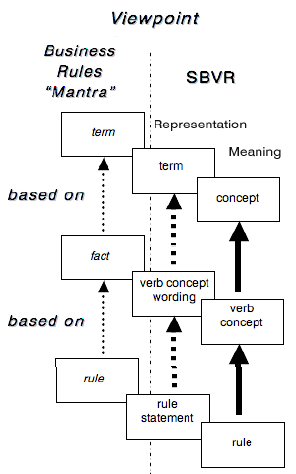 |
Terms
Facts
规则
|
Exercise ⌘。
- Choose concrete business problem (if you cannot thing of any, use Pizza Shop)
- Write down few terms
- Write down a couple of facts related to these terms
- Write a couple of rules based on the facts
Rule vs Fact ⌘。
- Method 1
Term: Boss, Employee
Fact: Employee has exactly one boss
Rule:
Employee reports to their boss
- Method 2
Term: Boss, Employee
Fact: Employee has Boss
Rule:
Employee has exactly one boss
Employee reports to their boss
Fact or Rule? ⌘。
- VAT is 6%
- 增值税税率为6%
- Square area formula is X^2
- 平方面积公式为x 2
- Buy one get one free
- 买一送一
- Employee must not work longer than 8 hours a day
- 员工工作时间每天不能超过8小时
Rule Engine ⌘
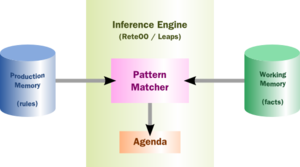
- The Rules are stored in the Production Memory
- Facts that the Inference Engine matches against are kept in the Working Memory.
- Facts are asserted into the Working Memory where they may then be modified or retracted.
- A system with a large number of rules and facts may result in many rules being true for the same fact assertion; these rules are said to be in conflict.
- The Agenda manages the execution order of these conflicting rules using a Conflict Resolution strategy.
规则引擎 。
- 这些 规则 保存在Production Memory里
- 推理机(Inference Engine)针对Facts进行匹配, Facts存在于“工作内存”(Working Memory)里.
- Facts 在工作内存中经过断言(asserted)后,可以被 modified 修改 or retracted 撤回.
- 如果一个事实和多个规则同时匹配
- 那么这时这些规则叫做发生冲突(to be in conflict).
- The Agenda是一个列表, 通过使用Conflict Resolution策略,来管理发生冲突的规则的激活顺序
Rules in Conflict 发生冲突的规则。 ⌘
- Facts
- Customer is a not-for-profit that also is a returning customer
- 客户是非盈利组织,同时是一个回头客
- Rule 1
- Non-for-profit customer receive 20% discount
- 非盈利组织客户打8折
- Rule 2
- Returning customer receive 10% discount
- 回头客打9折
The simplest rule Engine ⌘。
while HAS RULE TO FIRE
for each FACT
for each RULE
if FACT matches RULE than FIRE RULE 当有规则可以激活的时候
遍历事实
遍历规则
如果事实匹配规则,那么激活规则执行方法 Methods of Execution ⌘。
- 前向链接(Forward Chaining)
- 反向链接(Backward Chaining)
- 混合规则系统(Hybrid Rule Systems)
Forward vs Back Chaining ⌘。
Goal: determine which things can be transported together (human is a thing)
目标:这写东西可不可以在一起运输
- Facts
WangHao (type human) Bernard (type human) Water (type element) Computer (type element) Uranium (type element, radioactive == true)
- Rule
human is a mammal 人类是哺乳动物 mammal is a living organism 哺乳动物是有生命的生物体 living organism shall not be transported with radioactive elements 有生命的生物体不能和放射性物质一起运输
- Forward Chaining
Execution (Inference): human is mammal mammal is living organism computer is not living organism water is not living organism Derived Fact: human is living organism Conclusion: Wanghao (human) cannot be transported with Uranium (element, radioactive == true)
- Backward Chaining
Conclusion: Wanghao (human) cannot be transported with Uranium (element, radioactive == true) Explanation: goal human is living organism subgoal human is mammal subgoal mammal is living organism
Forward Chaining ⌘
- "data-driven" and thus reactionary,
- Facts are asserted into working memory
- One or more rules being concurrently true and scheduled for execution by the Agenda. starts with a fact, it propagates and end in a conclusion.
前向链接 。
- "数据驱动"从而reactionary,
- Facts经过断言进入工作内存
- 一或多个规则同时为真并由the Agenda计划执行。从一个fact开始, 不断传播下去,直到得出结论
Backward Chaining ⌘
- "Goal-driven"
- Starts with a conclusion which the engine tries to satisfy.
- If it can't it then searches for conclusions that it can satisfy (subgoals),
- Subgoals will help satisfy some unknown part of the current goal
- It continues this process until either the initial conclusion is proven or there are no more subgoals.
- Prolog is an example of a Backward Chaining engine
反向链接 。
- "目标驱动"
- 从结论开始,结论即引擎要证实的结论
- 如果不能证实(得到结论),那么将搜索可以满足的结论(子目标)
- 子目标可以帮助满足当前目标的一些未知部分
- 引擎不断重复这个过程直到最初结论得到证实或者不再有子目标可以证实
- 比如Prolog就是一个反向链接引擎
Why use a Rule Engine ⌘
- When should you use a rule engine?
- What advantage does a rule engine have over hand coded "if...then" approaches?
- Why should you use a rule engine instead of a scripting framework, like BeanShell?
为何使用规则引擎 。
- 何时应该使用规则引擎?
- 规则引擎比手写代码"if...then"的办法有什么优势?
- 为什么用规则引擎,而不用脚本(scripting), 例如BeanShell?
Advantages of Rule Engine ⌘
- Declarative Programming ("What", not "How")
- We can see "how" engine solved the problem
- Logic and Data Separation (breaking OO coupling of data and logic)
- Speed and Scalability (Rete, Leaps, PHREAK)
- Centralization of Knowledge (Documentation)
- Tool Integration
- Explanation Facility
- Understandable Rules (DSL)
规则引擎的优势 。
- 声明式(declarative)编程 (用户想的是“什么”,而不是“怎么做”,"What", not "How" as in 命令式(imperative)
- Can use on multiple platforms (Java, .NET, etc...)
- Upgrading Engine can speed up rules (e.g. Drools 5.0 -> 6.4) - you can optimise it yourself
- Engine chooses method of solving he problem (RETE, PHREAK, etc...)
- 可以看见引擎如何解决问题
- 逻辑数据分离 (打破了面向对象的逻辑数据耦合)
- 速度和扩展性 (Rete, Leaps, PHREAK)
- 知识集中化 (文档化)
- 集成工具
- Explanation Facility
- 规则易于理解 (DSL领域特定语言)
When should you use RE? ⌘
- The problem may be complex (no non-fragile way of building a solution for it)
- The problem is beyond any obvious algorithmic solution
- The logic changes often
- Domain experts (or business analysts) are readily available, but are nontechnical
- There are too many rules to manage them in the code
- We need rules to be explicit and documented
何时该使用规则引擎? 。
- 问题复杂 (一时找不到稳妥的解决方法)
- 问题超出一般明显的解决算法
- 逻辑经常变动
- 领域专家(或者业务分析员) 在身边, 但不懂技术
- 代码中有太多规则
- 需要规则显式说明并有文档记录
When shouldn't you use RE? 何时不该用规则引擎? 。⌘
- Maintaining the infrastructure/integration is more expensive than the gains
- 维护和集成框架成本过高 (安装,维护,安全补丁,升级,etc)
- With system which hardly ever change
- 系统几乎不会改动
- There is no person understanding RE
- 没有人懂规则引擎
Also see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AI_winter
Alternatives to Rule Engine 其他选择 。⌘
- Scripting 写脚本
- Decision Tables (Lookup tables) 决策表 (see OMG DMN)
- Decisions Tree 决策树
- Other data-driven solutions 其他数据驱动(data-driven)解决方案
Strong and Loose Coupling ⌘
How to determine rules may not be most suitable?
- Strong coupling
- "firing" one rule will clearly result in another rule firing, and so on;
- there is a clear chain of logic
- Decision Tree or process should be used
- Loosely coupling
- rules to be changed, removed and added without requiring changes to other rules
强耦合和弱耦合 。
如何知道使用规则引擎是否是合适?
- 强耦合
- 当一个规则激活("firing")将明显的导致另一个规则激活
- 有一个很清晰的逻辑链
- 可以用手写代码,决策树,过程
- 弱耦合
- 规则允许被改动,删除和添加,而且这么做不牵扯改动其它规则
Rules Examples ⌘
- Rules are the guidelines which instruct people what to do when certain conditions happen
- When the booking form arrives, then we send the confirmation letter
- When there are no bookings 14 days before the course commences, then we cancel the course
规则举例 。
规则就是一些准则,用来决定在一定条件下做什么
- 当收到预定表时,发送确认信
- 当课程开始前14天仍然没有任何预定,取消课程
Rules Syntax 规则语法 。⌘
When (if) Then
条件 (condition) 行动 (action)
Left side Right side
LHS (Left Hand Side) RHS (Right Hand Side)
举例 Example
如果下雨 拿雨伞
if it rains take an umbrellaAction 。⌘
Action can be
- Pure calculation or proper function, no IO involved | 简单的函数,(没有IO,没有太重的消耗资源的应用)
- INSERT (ASSERT) new fact(s) - 插入新的Facts
- UPDATE (MODIFY) existing fact(s) 更新存在的Facts
- DELETE (REVERT) existing fact(s) 删除存在的Facts
- Action shall not use external system
- 行动不应该用外部的系统
Bad and Good Actions 。⌘
WHEN
WRONG PASSWORD 3 TIMES
THAN
SEND EMAIL WHEN
WRONG PASSWORD 3 TIMES
THAN
INSERT ACTION_SEND_EMAIL_ACTION_FACTSample PHP code ⌘。
function _course_date_calculate_prices($course_date_node){
for($i=1; $i <= PUBLIC_COURSE_MAX_USERS; $i++){
$prices[$i]['suffix'] = " " . variable_get('nobleprog_currency','GBP') .' ' . t("per person") . ". " ;
$prices[$i]['value']= course_date_course_price($course_date_node,$i);
}
course_date_prices_apply_discounts($prices, $course_date_node);
return $prices;
}
function course_date_course_price(&$node, $number_of_delagets = 1){
$node_training = node_load($node->field_public_training[0]['nid']);
//If course doesn't have price, get it form the outline
if(is_numeric($node->field_course_price[0]['value'])){
$price = $node->field_course_price[0]['value'];
} else {
$price = $node_training->field_public[0]['value'];
}
if($number_of_delagets >= 2){
$discount_per_next_delegate = variable_get('discount_per_next_delegate',DISCOUT_PER_NEXT_DELEGATE);
$price = $price - ($price * $discount_per_next_delegate * ($number_of_delagets - 1) );
$price = round($price,-1);
}
return $price;
}
//apply a discount once the first booking has been made
//this stuff should work only
if('booking_form' == $node->type and $op == 'insert') {
$date_node_id = $node->field_course_date_id[0]['nid'];
if(is_numeric($date_node_id)){
$course_date_node = node_load($date_node_id);
if($course_date_node->type == 'course_date'){
//If the manual discount has been applied don't touch it
//this may be done manualy of by this very function
$now = date('Y-m-d');
$course_start_date = $course_date_node->field_course_date[0]['value'];
$month_before_the_course = date('Y-m-d',strtotime( $course_start_date . "- 1 month"));
if(! $course_date_node->field_course_price[0]['value'] > 0 ){
$course_outline_node_id = $course_date_node->field_public_training[0]['nid'];
$course_outline_node = node_load($course_outline_node_id);
$course_outline_price = $course_outline_node->field_public[0]['value'];
$early_booking_discount = variable_get('nobleprog_early_booking_discount',EARLY_BOOKING_DISCOUNT);
$course_date_node->field_course_price[0]['value'] = $course_outline_price * (1-($early_booking_discount+0.02));
node_save($course_date_node);
}
}
}
}Rules written in English 。⌘
- If you book the course one month before it commences, apply a 10% discount
- 如果你在课程开始的1个月前预定课程,将享受减10%的优惠
- If the course is booked (be the same company), the next person booking will have a 12% discount (no matter what the time is when they book)
- 如果课程已经预定了,那么下一个人预定将享受减12%的优惠
Fact Type vs Facts | 事实类型vs事实(Facts) 。⌘
- Facts are the data needed to check the condition
- Facts是用来检验条件满足与否的数据
- Facts can be modified by the rule Engine
- 规则引擎可以更改事实
- Fact Type is the structure of the Fact
- Fact Type ~ Class/Field;
- Fact ~ Object/Value
- For the rules above
- original price 原价 (e.g. fact: Course 1 price is 100 RMB)
- current date 当前日期
- course has been booked 课程已预定了
- commencement date 开始日期
- number of participants 报名数量
- price 价格
Rule Language ⌘。
Rule "Is Early Booking"
When
$CommencmentDate > $CurrentDate + 1 month
$course has been booked == false
Then
$Price = $Price - $Price *10%
End
Rule "Is Booked "
When
$Course has been booked == true
Then
$Price =$Price - $Price*12%
EndDecision Table (Rules as Data) ⌘
| EarlyBooking | Booked | Discount |
|---|---|---|
| TRUE | TRUE | 12% |
| TRUE | FALSE | 10% |
| FALSE | TRUE | 12% |
| FALSE | FALSE | 0% |
Facts as Objects - Java Beans ⌘。
public class BookingRequest {
private Boolean booked = true;
private Boolean earlyBooking = true;
private Float discount = new Float(0);
//getters and setters here
}
Business Rule (mvel) 。⌘
rule "Already Booked"
when
booking : BookingRequest( booked == "true" , discountValue : discount )
then
System.out.println("booked");
booking.setDiscount( discountValue + 0.12 );
update( booking );
end
rule "Early Booking"
when
booking : BookingRequest( earlyBooked == "true" , discountValue : discount )
then
System.out.println("early");
booking.setDiscount( discountValue + 0.1 );
update( booking );
end
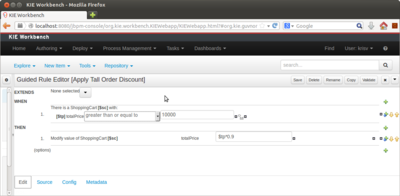
Guided Editor ⌘。
Domain Specific Language 领域特定语言(DSL) 。⌘
- Rule language (mvel or java dialects) may not be easy to understand by doctors or managers
- 规则语言 (mvel 或者 java dialects) 对于医生和经理可能不太容易理解
- Certain phrases like $now <= $start can be expressed much clear in English (event has started)
- 一些意思的表达比如 $now <= $start 用英语表达更加清楚 (event has started)
DSL Example。⌘
expander sample.dsl
rule "Already Booked"
when
booking : BookingRequest( booked == "true" )
then
booking.setDiscount( 0.12 );
update( booking );
end
rule "Already Booked"
when
Booking request:
- has been booked
then
set discount to 0.12
end
Changing Rules Into DSL ⌘
- Unit test the rule
- Create a DSL file
- Changed the extension from .drl to .dslr
- Add expander clause into dslr file ( expander DiscountDSL.dsl)
- Prefix all lines with ">" charater
- Change your rules write DSL rules line by line
将规则改为领域特定语言(DSL) 。
- 单元测试规则
- 建立DSL文件
- 更改扩展名 .drl 为 .dslr
- 添加 expander 语句到 dslr 文件 (expander DiscountDSL.dsl)
- 在所有行行首添加 ">" 符号
- 一个一个地改变你的规则
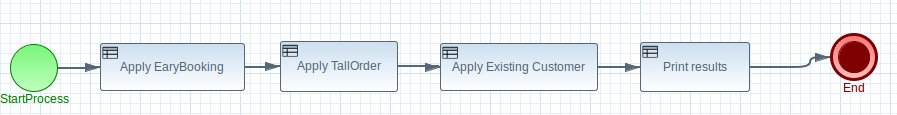
RuleFlow/Process ⌘。
- Rules are fired without defined order
- 规则的启动没有启动顺序
- If too many rules depend on the result of the other, complexity may become hard to maintainable
- 如果太多规则依赖另一个规则的结果,可能变得难以维护
- If rule should be invoked only after certain stage is reached then RuleFlow/BPMN is useful
- 几乎所有的项目,两者都用
- 把逻辑用显式的方式写出来
Fusion ⌘。
- Already part of KIE, don't need to install anything
- Enabled by declaring a fact as an event @role(event)
- Event has start time and can have interval
- 事件有起始时间还有时间间隔
- three most features
- Temporal Operators (before, after, ends....)
- Aggregation using Time Window
- Stream Mode
Fusion Use Cases | Fusion 案例 ⌘。
- Using operators
- Trainer should not be assigned to teach two courses at the same time
- 培训师不可以同时培训两门课
Course1 overlaps Course2
- Aggregations (Time Window) 聚合
- Trainer shall not teach more than 40 hours in any 30 day window
- 培训师在三十天内总课时不能超过40小时
accumulate( $c: Courses(trainer_name="WangHao",$d : duration) over window:time( 30d ), $duration :sum($d)) eval($duration > 40h)
- Streaming Mode with Moving Window
- When sales exceeds 3 bookings per coordinator per day, send warning to managers
- 如果一个培训专员每天收到的订单超过3个,那么给经理发出警告
- If share price falls 10% in less than an hour, sell of all shares
- 如果股票价格在一小时之内跌过10%,那么卖出全部的股票