Administering Drupal 8 Website
- title
- Administering Drupal 8 Website
- author
- Lukasz Sokolowski (NobleProg Ltd)
Administering Drupal 8 Website Training Materials
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
Intro
- What is Drupal?
- The Building Blocks of Drupal
- Choosing and managing your themes
- Choosing and managing your modules
- Managing your content
- Ordering your content
- Managing your users
- Troubleshooting Drupal
What is Drupal
- Community
- Software
- CMS
- Framework for other project
- e-commerce
- social networks
- portals
- media portals
- LMS, CRM, ERP, etc...
Drupal Sandbox
- Demo - (http://simplytest.me/)
- DDEV - (https://ddev.com/)
- Overall docs - https://www.drupal.org/docs/develop/local-server-setup
- Specific for drupal(l)s - https://ddev.readthedocs.io/en/stable/users/quickstart/#__tabbed_4_3
- Good alternatives
- Lando - (https://docs.lando.dev/)
- Docker4Drupal - (https://wodby.com/docker4drupal)
- Docksal - (https://docksal.io/)
- Bitnami - (http://bitnami.org/stack/drupal)
- AmazonEC2, and other hosting options
Building Blocks
|
Extensions
|
Users
|
|
Content
|
Structure
|
Extensions
Themes, Profiles (Distributions) and Modules are also known as Extensions.
Distributions
A Distribution contains:
- Drupal core
- Contributed modules
- Themes
- Pre-defined configuration
Examples:
- Bear (an alternative to the Minimal or Standard profiles)
- Varbase (good starterkit)
- Open Social (social communities and intranets)
- Commerce Kickstart (e-commerce, https://install.commercekickstart.com/)
- ELMS (e-Learning Management System)
More: http://drupal.org/project/distributions
Finding Admin Settings
- go to admin/index
- use ctrl+f (search option in the browser) to find the option you need
Drupal core versions
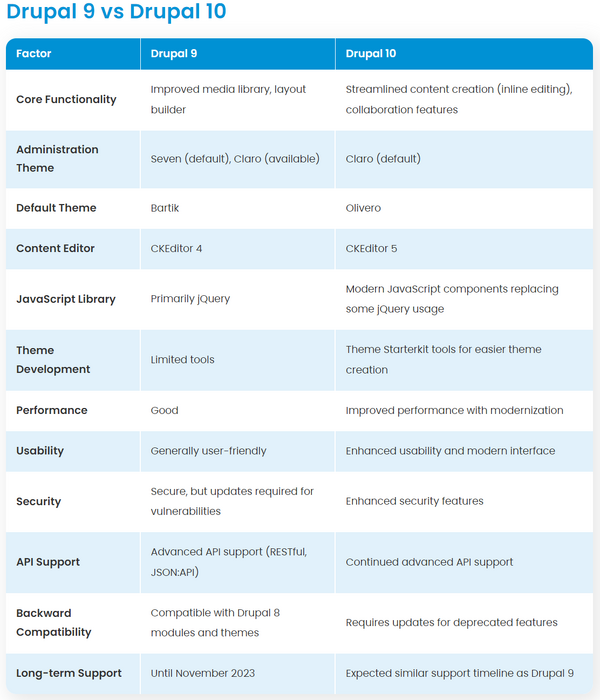
10 vs 11
| Feature | Drupal 10 | Drupal 11 |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Technology | Symfony 6 | Symfony 7 |
| PHP Requirement | PHP 8.1+ | PHP 8.3+ |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
/* Feature Drupal 10 Drupal 11 Underlying Technology Symfony 6 Symfony 7 PHP Requirement PHP 8.1+ PHP 8.3+ User Interface Modernized, but limited Modernized and enhanced admin UI, with a new navigation system Component Development Module-based Stable Single Directory Components (SDC) included in core Content Modeling Basic content moderation Easier content modeling and enhanced content moderation workflows Site Building Standard features APIs for "Recipes" to build sites with pre-packaged feature sets Performance Performance improvements over Drupal 9 Further optimizations, including faster page performance and lazy loading Automatic Updates Experimental in some modules Stable and fully integrated into core File and Media Management Standard features Improved file and media management
- /
Modules
"Extend and customize Drupal functionality"
- Contributed Modules are developed by Drupal community
- Custom Modules are not published to third parties
- Core Modules are provided by the Drupal Core
- During this course we focus on the Core Modules
Some modules are much bigger and more complex than the core!
Modules Versions
- Important when you are looking for Documentation and Help
- Security Upgrades
Modules Support
- Issues
- Statistics
- Documentation
Useful core modules
- Book
- Actions
- Forum
- Aggregator
- Translation-related
Exercise 1
Installing modules - Translate the website into another language (core module 'Language') - Create simple blog (contributed 'Blog' module)
Themes
"Allow you to change the look and feel of your Drupal site."
- Contributed Themes
- Custom Themes
- Sub-themes
- Blocks configuration can change when you change your theme
- Administration Theme
- You can allow users to change your theme
Theme Configuration
- admin/appearance/settings
- Customizing colours (color module)
- Configurations depends on the theme
Exercise 2
Installing themes - Choose and install a suitable Drupal theme - Set your admin theme to Bartik
Content
- Entities
- Nodes
- Files
- Taxonomy
Entities
- Entity types in core
- Configuration Entity
- Used by the Configuration System
- Supports translations and can provide custom defaults for installations
- Content Entity
- Consist of configurable and base fields
- Can have revisions and support translations
- Configuration Entity
- Bundles (sub-types)
- Configuration Entities that enhance a Content Entity
- Their configuration stores the differences between the content entity types, such as settings and fields
Entities Con't
Entity Structure Examples
|
Content Entity Types:
|
Configuration Entity Types:
|
Nodes
- Structure/Content types (admin/structure/types)
- Content vs Content Types
- Node can mean either, though Node Type is used as well
- Each Content type can differ
- Fields
- Workflow
- Permission
- Autopath and Menu options, etc...
Fields
- Field Type vs Field Widget
- Common types are Text, Number, Date, Email, Location, etc...
- Visibility in Teaser (Summary) and Full Node
Exercise 3
Creating content - Create two or three content pages (use the default content type Basic Page) - Create one Article, related to your company
Revisions
- Create new revision by default
- Log message
- Reverting
- Diff Module*
Exercise 4
Time vehicle - Edit existing basic page and add new line of text in the Body field - Change it again and add another line, same field - Revert it to the very first version - Compare version 2 and 3 (diff)
Comments
- Moderation
- Status
Exercise 5
Creating comments - Allow all users to comment basic pages - Comment one of them - Answer to that comment
Workflows
- Unpublished means visible to the author and administrators/moderators
- Content can be unpublished by default
- Content Moderation (Now finally stable part of the core)
Files
- Uploading
Images
- Images can be handled via WYSIWYG or Image Field
- Configuration/Media/Image Styles (admin/config/media/image-styles)
- Assign a style to Display settings in a content type
Exercise 6
Content types - Create your own content type, related to your company -- add at least 2 new fields, with different type of field -- add some pictures to your pages (use proper field type) -- make it appear-able in menus: Tools, Footer -- should be unpublished by default, added to the front page and sticky
Taxonomy
- Vocabularies and Terms
- HS, Taxonomy Menu*
Exercise 7
Playing with categories - Create new vocabulary related to your own content type -- Add some terms (at least 3) - Create new post and apply some taxonomy
Users
- User Accounts settings (admin/config/people)
- Email Templates
- Fields
- Profile2*
- Roles and Permissions
- Creating Roles
- Granting Permission
Exercise 8
Handling users - Create a role for only 'Basic Page' editor and assign all necessary permissions - Set permissions so only authenticated users can comment and create your content type
Structure
Blocks
- Structure/Blocks (admin/structure/block)
- Blocks are part of the structure NOT content
- No search
- No revisions
- No workflow (publish/unpublish)
- No authorship information
- No fine-grained permission for editing blocks
- No index support (search)
Exercise 9
Blocks - Position some blocks in your theme - Set which pages certain blocks should appear upon
Menus
- Structure/Menus
- Menu vs Menu Item
- Create when editing the content
- Primary/Secondary Menu
- Two menu items to the same content
Exercise 10
Menus - Build a menu for your website - Add your own type nodes to the menu (you can do this by editing the nodes too)
Text Formats (Input Filters)
- Configuration/Content Authoring/Text Formats (admin/config/content/formats)
- Text Formats allow to filter and transform text when saving and viewing a field
- Keep it Simple
- Rules can overlap with WYSIWYG
Display modes
Content, Custom block, Comment, Taxonomy term, User - they can have:
- Form modes
- View modes
Contact forms
Simple default forms to serve the feedback for the site, etc
Views
- Provides a back end to fetch information from the database
- content, user accounts, taxonomy terms, and other entities
- Can present it to the user as filtered
- a grid, HTML list, table, unformatted list, etc.
- Use cases
- Adding functionality to administrative pages
- Expanding functionality via contributed projects
- Improving table accessibility
- Working with multilingual views
Exercise 11
Views - Create new view with nodes only from your own content type -- allow users to filter it via one of the fields
Admin Tasks
- Configuring Search
- Cron
- Customizing Error Messages
- Maintenance(site offline)
- URL Aliases
- Reporting
- Configuration management
Exercise 12
URL Aliases - Make your url aliases to work auto-magically (contributed module 'pathauto')
Additional Exercises
MODULES 1. Install 'book' module and create simple wiki about your company - create one book with at least 3 pages 2. Make your website a little bit smarter/automatic - it should send email to you, each time when the basic page will be created (actions, rules) THEMES 1. Add Mayo theme and play with it's many configuration options - chose color set 'Tricolor' - change font family to 'Verdana, geneva..' - make default fonts bigger (18px) - provide rounded corners to frames (blocks and content) - add font resizing controls to the header CONTENT 1. New content type - Install the Field group module - Create a content type called Booking - Add two fields, From and To, of type Date - Create group of newly added fields called Dates (https://www.drupal.org/project/field_group) 2. Create relationship between 2 content types - make them both link-able STRUCTURE 1. Block - Create your own Custom Block Type (My Block Type) - Create block using this type and place it in Footer 2. Menu - make your Main menu nicer (https://www.drupal.org/project/tb_megamenu) 3. Taxonomy - Create 2 taxonomies with relation between them - Apply it to the basic pages 4. Views - Create view with Basic Pages and some data from related Articles (make a content reference)