SOA Concepts
- Service
- ESB
- Loose Coupling
- Policies and Processes
- Web Services
- SOA Strategy
- Governance
Service
A service is a piece of self-contained business functionality. The functionality might be simple (storing or retrieving customer data), or complex (a business process for a customer’s order). Because services concentrate on the business value of an interface, they bridge the business/IT gap.
ESB
- ESB is the infrastructure that enables high interoperability between distributed systems for services.
- It makes it easier to distribute business processes over multiple systems using different platforms and technologies.
- TCP network + DNS may be consider a type of ESB
Loose Coupling
- Concept of reducing system dependencies.
- Minimize the effects of modifications and failures.
- Price for loose coupling: complexity.
- Loosely coupled distributed systems are harder to develop, maintain, and debug.
Policies and Processes
You need clearly defined roles, policies, and processes
- service lifecycle
- implementing model-driven service development
- set up several processes for distributed software development.
- agile project management
Web Services
- Web Services are one possible way of realizing the technical aspects of SOA
- Web Service can be based on SOAP or REST
Governance and Management support
- Central team that will determine general aspects of your specific SOA.
- The ultimate goal is decentralization
- Right people (large systems are different from small systems)
- Requirements driven development
- You need support from the CEO and CIO. SOA is a strategy that affects the company as a whole.
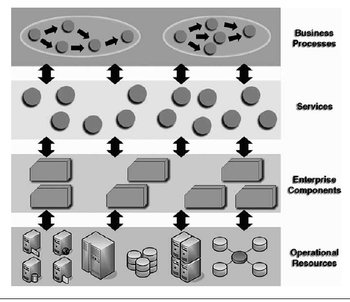
Technical Concept of SOA
- Services
- Interoperability
- Loose coupling
SOA Ingredients
- Infrastructure
- Architecture
- Processes
- Governance
SOA Terminology
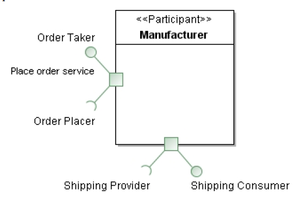
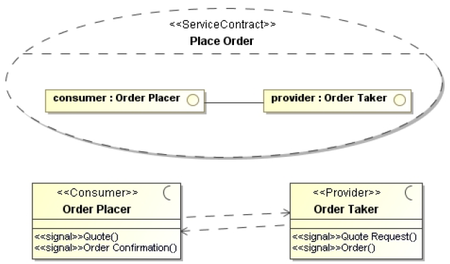
- A provider is a system that implements a service (a business functionality) so that other systems can call it.
- A consumer is a system that calls a service (uses a provided service).
- Other names: requestor, client, server....
- A participant (AKA service agent) is either a provider or a consumer
SoaML Notation
Another definition of SOA
SOA is an architectural paradigm
- for dealing with business processes
- distributed over a large landscape of existing and new
- heterogeneous systems
- that are under the control of different owners.
Different Perspective
Questions
- What are the three technical concepts of SOA?
- What are the key ingredients of SOA?
- Is SOA a technology?
- What is the difference between services and web services?
- Does SOA have to use Web Services?