SBVR
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- SBVR
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
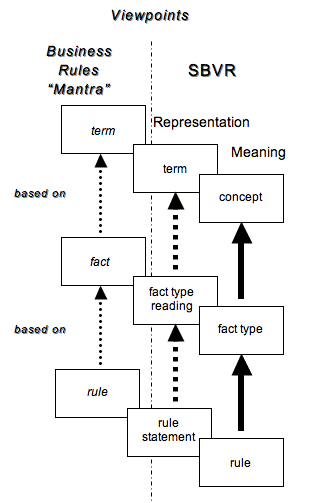
What is SBVR ⌘
- Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules
- adopted standard of the OMG intended to be the basis for formal and detailed natural language declarative description of a complex entity
- formal vocabularies and rules can be interpreted and used by computer systems
- can be exchanged via XMI
- part of MDA
- integrate with other standards (notably BMM and BPMN)
Overview ⌘
SBVR defines:
- vocabulary
- rules for documenting the semantics of business vocabularies
- business facts
- business rules
- XMI schema for the interchange of rules and vocabularies between organizations and tools
- MOF compliant
Some tools which implement SBVR ⌘
- Fico
- opaals
Facts and Rules ⌘
- fact types - Trainer delivers Courses
- business rules - trainer must be interviewed before delivering first course
- facts can be derived - if Person 1 is a brother of Person 2 therefore Parents of Person 1 are parents of Person 2
Rule Statements ⌘
- Structural Business Rules use two alethic modal operators:
- it is necessary that … (… always …)
- it is possible that … (… sometimes …)
- it is impossible that … (… never …)
- Operative Business Rules use two deontic modal operators:
- it is obligatory that …(… must …)
- it is prohibited that … (… must not …)
- it is permitted that … (… may …)
Rule writing styles ⌘
- Prefixed Rule Keyword
- e.g. It is necessary that the associate trainer singes the associate trainer agreement
- Embedded (mixfix) Rule Keyword
- e.g. Associate trainer always has associate trainer agreement signed
Independence ⌘
- Rule Independence (from processes and events)
- Enforcement
- Methodology and Notation