Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
- The infrastructure of a SOA landscape that enables the interoperability of services.
- Its core task is to provide connectivity, data transformations, and (intelligent) routing so that systems can communicate via services.
- ESB is just a piece of software, hardware is not part of ESB.
ESB Responsibilities
- Providing connectivity
- Data transformation
- (Intelligent) routing
- Dealing with security
- Dealing with reliability
- Service management
- Monitoring and logging
Interoperability through transformation
- May transfer any protocol to any protocol
- May change the formats or mappings
- May contain transformation logic
- Should not contain business logic
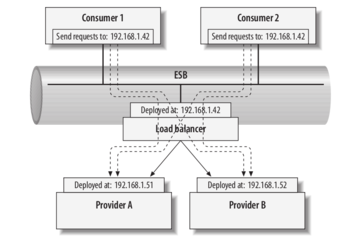
Routing
- There must be some way of sending a service call from a consumer to a provider, and then sending an answer back from the provider to the consumer
- Depending on the technology used, and the level of intelligence provided, this task may be trivial, or may require very complicated processing
Interceptors
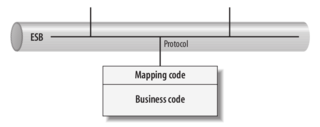
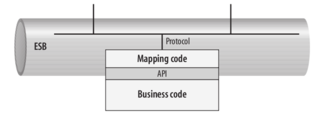
Protocol-Driven Versus API-Driven ESB
Other Important Concepts
- Point-to-Point Connections Versus Mediation
- Data Mapping
- Security
- Reliability (message delivery and queueing)
- Service Management (replaces UDDI)
- Monitoring and Logging
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
- Shows the state of your business on the fly
- Analyses activity rather than data (compare data warehouse and data mining)