UML 2 Introduction
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- UML 2 Introduction
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (bs@NobleProg.co.uk)
</slideshow>
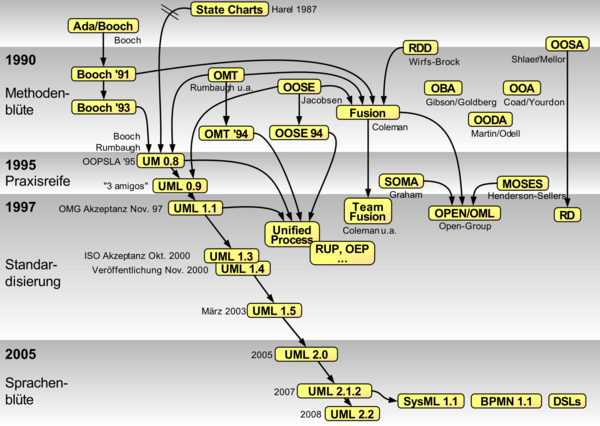
History of UML⌘
Overview⌘
- OMG Standard
- The Unified Modeling Language (UML)
- Data modeling, business modeling (work flows), object modeling, and component modeling
- UML aims to be a standard modeling language which can model concurrent and distributed systems
- UML is a de-facto industry standard
- UML models may be automatically transformed to other representations (e.g. Java, PHP) by means of QVT-like transformation languages
- UML is extensible, through profiles', stereotypes and tagged values
- A lot of other languages are based on UML (SysML, SoaML)
- Usually default language for a lot of architecture frameworks (MoDAF, DoDAF, NAF)
UML Specification ⌘
- http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.5/
- Object Constraint Language (OCL) http://www.omg.org/spec/OCL/
- UML Diagram Interchange
UML Features⌘
- Does not define method (see Unified Process)
- UML defines both:
- UML model (contains documentation and all relations)
- UML diagrams (partial graphic representation of a system's model)
- UML can model both views of the system:
- Static (structural)
- Dynamic (behavioural)
- From 2.4.1 complete machine-readable definition of the language is available
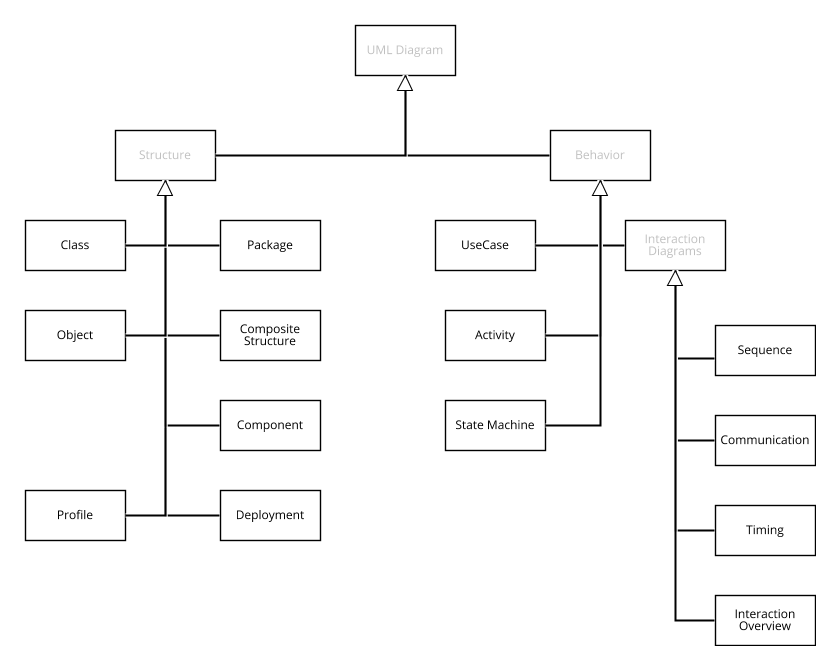
- Contains 14 different diagarams
UML Diagrams ⌘