Enterprise Architecture and Management
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Enterprise Architecture and Management
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (bs@NobleProg.co.uk)
</slideshow>
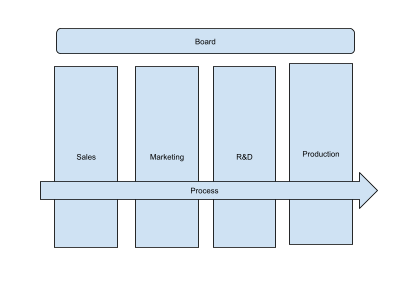
Function vs Process Orientation ⌘
Business Process Concepts ⌘
- Business Process Reengeneering (BPR)
- Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Six Sigma
TQM⌘
- Focus on work process
- Quality problems are mostly dependent on the work processes that designed and manufactured the products and services
- Analysis of variability
- Uncontrolled variances are the primary causes of quality problems, and these variances should be analyzed and controlled by the front-line workers
- Management by fact
- Quality improvements programs should be based on systematic data collection, analysis and experimentation for solution implementation
- Learning and continuous improvement
- Quality improvement is never-ending and employee learning is a major part for carrying out quality improvements
William Edwards Deming⌘
- The father of TQM
- 1900 – 1993
- American statistician, professor, author, lecturer, and consultant
- National hero in Japan
- Unknown it the US until 1970s
System Thinking⌘
- A highest level unique approach to problems solving and managing the complexity.
- It views certain 'problems' as a part of the overall system so focusing on these outcomes further develops the undesired element or problem.
- E.g. Instead of optimizing how to print invoices (focusing on a single function), we can simply send them electronically to the buyer system (thinking in terms of the whole process and impact of the system)
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR)⌘
- Management philosophy to enhance corporate competitiveness
- M. Hammer – he believed corporation were simply automating processes design prior to the wide usage of computers
- The key enabler for BPR is IT
- IT serves as the disruptive technology that allows generalists to do the work traditionally performed by specialists, enables everyone to make decisions
- "Don't automate, obliterate"
- Illogical business activities are there because nobody dares to challenge them
Michael Hammer⌘
- Michael Martin Hammer (1948 - 2008)
- American engineer
- Management author (has he ever managed something?)
- Professor of computer science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- Known as one of the founders of the management theory of Business process reengineering (BPR)
Lean ⌘
- Lean manufacturing
- Lean IT
- Lean software development
- Lean Services
- Lean Integration
Lean Principles
- Eliminate waste
- Amplify learning
- Decide as late as possible
- Deliver as fast as possible
- Empower the team
- Build integrity in
- See the whole
Lean ⌘
Waste in Lean
- Waste = Muda (無駄)
- unnecessary code and functionality
- delay in the software development process
- unclear requirements
- bureaucracy
- slow internal communication
- Unevennes = Mura (斑 or ムラ)
- Unreasonable = Muri (無理)
Processes and SOA⌘
- A BPM based system might create a tight coupling between integration technology and individual business applications
- This tight coupling increases the operational cost. Why?
- As a business process changes, the integration technology also changes
- BPM without services is:
- Complex and brittle, because the process layer is required to access the underlying business applications directly
- The SOA provides the ideal platform for the business process layer for the following reasons:
- A line of business services provides coarse-grained business functionality that map the business tasks in a business process
- Business process is not responsible for knowing any details of the underlying application and technology platforms
- Service contracts for the line of business services provide well-defined and unambiguous interfaces for accessing the services