SOAP
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Web Services Basics For Non-programmers
- author
- Pete George (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
Day One Schedule ⌘
- Introductions
- Service-Oriented Architecture
- Web Services Overview
- XML
- SOAP
SOAP ⌘
Learning Objectives
- To understand the place of SOAP in Web services
- To appreciate the advantages of using SOAP
- To understand the basic SOAP structure
- To explore SOAP requests and responses on a Web service
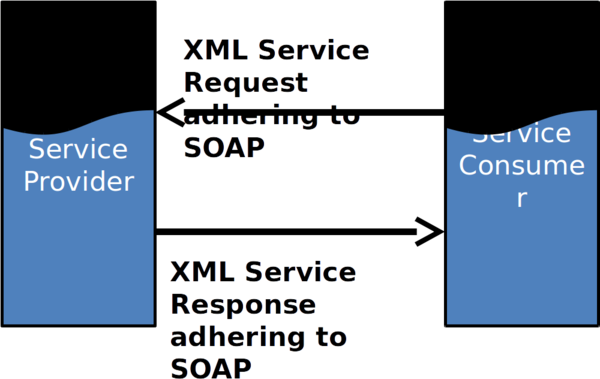
SOAP Protocol Messaging
SOAP Metaphor ⌘
- XML = Language of message
-English
- SOAP = Style of message
-Business letter
SOAP Definition ⌘
“a lightweight protocol for exchange of information in a decentralized, distributed environment” (W3C)
SOAP ⌘
- Originally: “Simple Object Access Protocol”
- Just “SOAP” since 1.2
- Protocol used for exchanging data
- Uses XML to describe information
- Usually uses HTTP(S) for transportation
Advantages of SOAP ⌘
- XML
- HTTP
- Additional Benefits
XML Benefits ⌘
- Interoperability
-Platform-neutral
-Language-neutral
-Vendor-neutral
- Easy to implement
-Minimum Web server + ASP page/CGI script
HTTP Benefits ⌘
- HTTP well known and used network protocol
- Firewall-safe
- Can use HTTP over SSL (HTTPS)
- NB: SOAP can use other transport protocols
Additional Benefits ⌘
- Robust
-Can create own XML structure
- Use other XML technologies
-E.g. XML-Signature for security
- Can use attachments
- Flexible
-Can represent complex messages
Can cope with messages being passed along a chain
SOAP Structure ⌘
- Envelope
-Container for message
- Header
-Information about the message
- Body
-The message
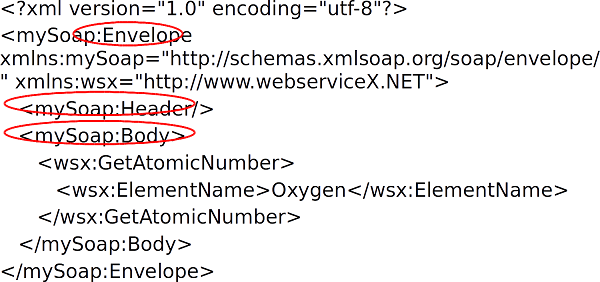
A SOAP Service Request ⌘
<Envelope> ⌘
<mySoap:Envelope xmlns:mySoap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.o rg/soap/envelope/" xmlns:wsx="http://www.webserviceX.NET">
- Root element for XML doc
- Lists namespace declarations, e.g:
-mySoap = SOAP XML namespace
-wsx = namespace for service provider
<Header> ⌘
<mySoap:Header/> (<mySoap:Header></mySoap:Header>)
- Optional
- Often omitted
- Could contain instructions for handling message
-e.g. user credentials
<Body> ⌘

A SOAP Service Response ⌘
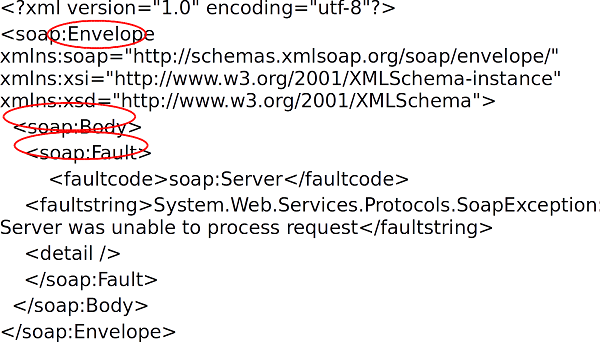
A SOAP Service Response - Fault ⌘
<Fault> ⌘
Summary Exercise ⌘
Using the JMeter test tool, send a request to the Periodic Table Web service
- Use Get Atomic Number to get the atomic number of Hydrogen
- Analyse the Service Response and identify SOAP structural elements: namespaces, root element, header, body, fault
- Investigate other methods/Web services available