Statistics for Decision Makers - 01.01 - Introduction
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="。" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" footer="www.NobleProg.co.uk" subfooter="Training Courses Worldwide">
- title
- 01.01 - Introduction
- author
- Bernard Szlachta (NobleProg Ltd) bs@nobleprog.co.uk
</slideshow>
Inference and Decision。
- Inference is about finding facts
- Decisions are about taking courses of action, which can be based on inference findings
Is inference not followed by a decision idle?
Decisions and Rules。
- A Decision is a choice between alternatives
- Rules are the conditions which guide or determine decisions
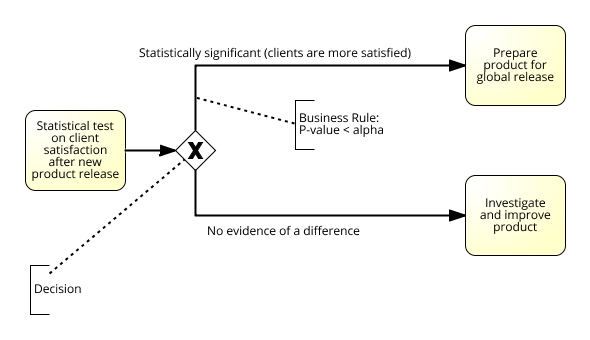
BPMN, Decisions and Statistics。
Statistics, Decisions and Rules。
- The Decision Maker encounters a decision point in a business process
- Making those decisions is mostly a question of judgement
- Finding evidence using the scientific method
- The ultimate goal is to fully automate decision making by creating rules which use statistical methods
Hiring Example。
- Business Process
- Recruitment
- Decision
- Invite a candidate for interview or not?
- Variables
- Candidate has relevant experience
- Salary expectation
- Availability
- Inference
- What is the probability that the candidate will be hired and make a good employee?
- Rules
Rule "Should the candidate be interviewed?"
When
P-value < 0.01
Then
Interview Candidate
End
Traditional Rules Example。
Rule "Should the candidate be interviewed?"
When
ExpectedSalary < 100000 and
AvailableDate < 2015-01-01
ExperienceScore >= 1000
Then
Interview Candidate
End
When to use Statistical Inference to make decisions。
- Deterministic solutions are usually cheaper and easier to understand and maintain
Use Statistical Models if:
- the loss related to errors caused by deterministic solutions justifies the cost of maintaining a statistical module
- there are no easy deterministic solutions
- the model needs to learn (e.g. neural networks)
- the rules are in the heads of managers who change often and need to relearn the rules each time from experience
Technical Statistics。
- Database Indexes (e.g. Oracle)
- Search Engine
- Network Routers
- .....
Overview of the methods。
| Describe | Sample | Measure | Predict |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Questions to the audience。…
- Why things differ each time we measure them?
- Brownian Motion
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Quiz。
Quiz