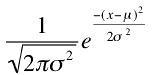- Most of the statistical analyses presented are based on the bell-shaped or normal distribution
- Methods for calculating probabilities based on the normal distribution
- A frequently used normal distribution is called the Standard Normal distribution (AKA Gauss Distribution)
- The binomial distribution can be approximated by a normal distribution
Bell Curve
- Gaussian curve is a special case of a Normal Distribution (μ = 0, σ = 1)
- Although Gauss played an important role in its history, de Moivre first discovered the normal distribution
- There is no "the normal distribution" since there are many normal distributions which differ in their means and standard deviations
Probability Density Function
=NORMDIST(1,0,1,FALSE) = 0.2419707245
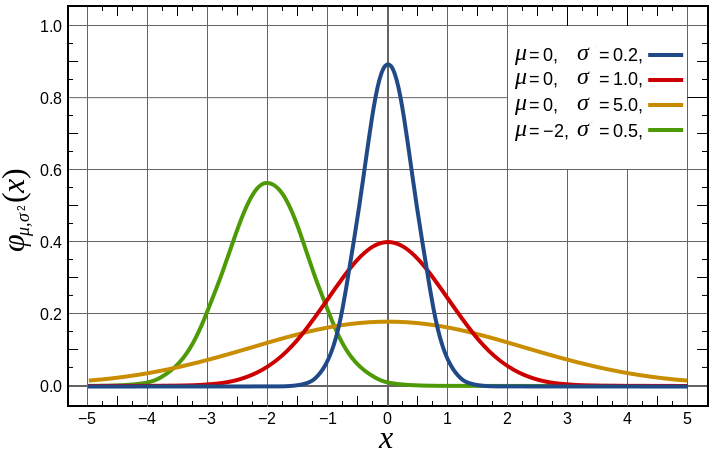
- All normal distributions are symmetric with relatively more values at the centre of the distribution and relatively few in the tails
The density of the normal distribution
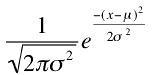
- The density of the normal distribution is the height for a given value on the x axis
- The parameters μ and σ are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, and define the normal distribution
- The symbol e is the base of the natural logarithm and π is the constant pi.
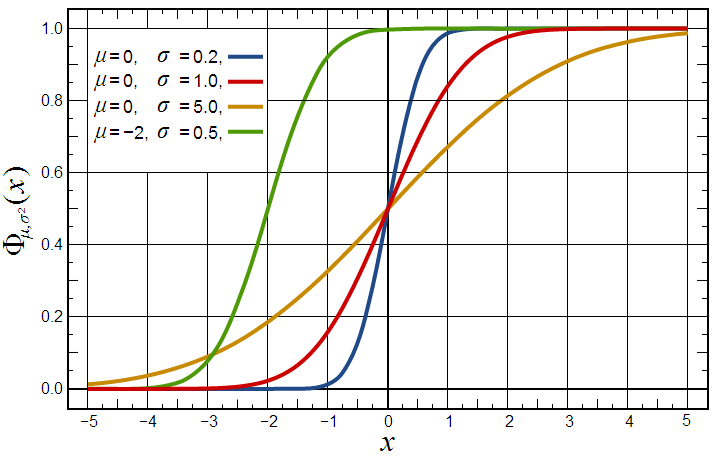
Normal Cumulative Distribution
Features of Normal Distributions
- Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean.
- The mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal.
- The area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0.
- Normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails.
- Normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ).
- 68% of the area of a normal distribution is within one standard deviation of the mean.
- Approximately 95% of the area of a normal distribution is within two standard deviations of the mean.
Quiz