Web Services
THIS IS A DRAFT
This text may not be complete.
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="false" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- WebServices with SOAP and WSDL Basics
- author
- Lukasz Sokolowski (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
WebServices with SOAP and WSDL Basics
WebServices with SOAP and WSDL Basics Training Materials
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
Overview of Web Services ⌘
What are they?
- application components
- communicate using open protocols (HTTP,SMTP,FTP,JMS,..)
- self-contained and self-describing
- can use SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
- can be described using WSDL (Web Services Description Language)
- can be discovered using UDDI (Universal Description, Discovery and Integration)
- can be used by other applications
- use XML as the basis
Definitions ⌘
- w3c
- from book
- w3schools
- examples
w3c ⌘
( http://www.w3.org/TR/ws-gloss/#webservice )
“A Web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. It has an interface described in a machine-processable format (specifically WSDL). Other systems interact with the Web service in a manner prescribed by its description using SOAP-messages, typically conveyed using HTTP with an XML serialization in conjunction with other Web-related standards.”
book ⌘
( "Web Services Essentials", Ethan Cerami )
"A web service is any service that is available over the Internet, uses a standardized XML messaging system, and is not tied to any one operating system or programming language."
Two additional properties of WS (not required, but desirable):
- self-describing with a general XML syntax
- discover-able by a plain find mechanism
w3schools ⌘
"Web Services can convert your application into a Web-application, which can publish its function or message to the rest of the world."
Examples of use ⌘
- Google services (translator, maps, etc.)
- Amazon FWS
- Oracle Courses for their partners (for example our NP site oracle-training-courses.com)
- Sharing calendars
- NobleProg Course Outlines
- rss news
- tracking (package, portfolio)
- credit card verification
Why do we need Web Services? ⌘
What are the benefits of using Web Services?
- The existing function is exposed on to network
- Interoperability - connecting different applications
- Standardized Protocol
- Low cost of communication
Two Types of Uses
- Reusable application-components
- Connect existing software
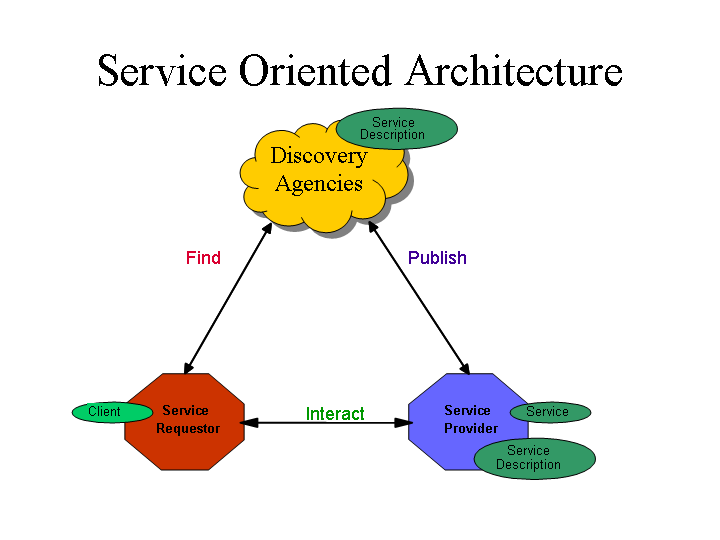
Service-Oriented Architecture Principles (SOA) ⌘
Service Oriented Architecture properties:
- Sensible view
- Information orientation
- Description orientation
- Granularity
- Network orientation
- Platform neutral
w3c Web Service Architecture Working Group ⌘
Web Service Architecture ⌘
- Essential part
- Interact between service provider and service requester
- This is the Web Service
- Interact between service provider and service requester
- Discover services need not be used
- They will become the interface to a world of data and query services
- Not just Web service
- They will become the interface to a world of data and query services
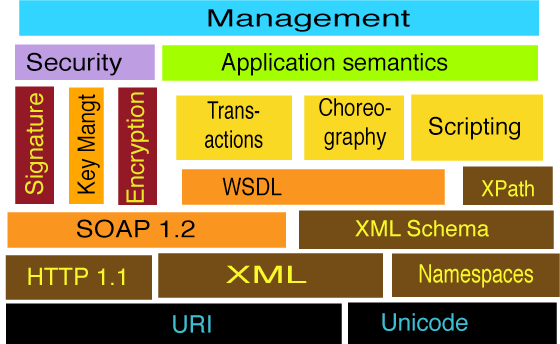
Web Service Stack ⌘
HTTP and XML - what is the whole buzz about? ⌘
XML messaging can be done in several ways:
- XML Remote Procedure Calls (XML-RPC)
- SOAP
- using just HTTP GET/POST and passing high-handed XML documents
XML ⌘
eXtensible Markup Language.
Transports and stores data.
Example of code
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<note>
<to>My grandma</to>
<from>Me</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body>Don't forget about grandpa's birthday!</body>
</note>
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) ⌘
SOAP is an XML-based protocol and allows applications to exchange information over HTTP.
There are two different ways of interpretation:
- Service Oriented Architecture Protocol
- in general, represents the information needed to invoke a service or reflect the results of a service invocation
- contains the information specified in the service interface definition
- Simple Object Access Protocol
- with SOAP RPC Representation, it's a method invocation on a remote object
- serialized list of arguments from this method, moved from local to remote environment
SOAP properties ⌘
- communication protocol
- format for sending messages
- designed to communicate via Internet
- platform independent
- language independent
- based on XML
- simple and extensible
- allows you to get around firewalls
- W3C standard
Web Service Description Language (WSDL) ⌘
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) files are XML documents that provide metadata for a SOAP service.
They contain information about the functions or methods the application makes available and what arguments to use.
By making WSDL files available to the consumers of your service, it gives them the definitions they need to send valid requests precisely how you intend them to be.
You can think of WSDL files as a complete contract for the application’s communication.
If you truly want to make it easy for others to consume your service you will want to incorporate WSDL into your SOAP programming.