Power Automate Office Scripts Basics: Difference between revisions
Lsokolowski1 (talk | contribs) |
Lsokolowski1 (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Cat|JavaScript}} | {{Cat|JavaScript}} | ||
;title: Power Automate Office Scripts Basics | ;title: Power Automate Office Scripts Basics | ||
;author: Lukasz Sokolowski | ;author: Lukasz Sokolowski | ||
| Line 29: | Line 26: | ||
* Connection to SAP GUI through Scripting Engine | * Connection to SAP GUI through Scripting Engine | ||
--> | --> | ||
* Troubleshooting | |||
* Exercises | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
'''<big>Office Scripts</big>''' | '''<big>Office Scripts</big>''' | ||
* '''Online''' version of ''VBA'' | * '''Online''' version of ''VBA'' | ||
* Built to ''' | * Built to run in '''Excel Online''' | ||
** similar to ''GoogleDocs App Scripts'', but based on '''TypeScript''' instead of ''Javascript'' | ** similar to ''GoogleDocs App Scripts'', but based on '''TypeScript''' instead of ''Javascript'' | ||
** '''TS''' is a '''subset''' of ''JS'', so we can use JS as well | ** '''TS''' is a '''subset''' of ''JS'', so we can use JS as well | ||
* More here | * Office Scripts are '''only available for Excel''' (no support in Outlook, Word, Access, etc) | ||
** for both - Online and Windows versions of excel | |||
* ''More here'' | |||
** <small>https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/overview/excel</small> | ** <small>https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/overview/excel</small> | ||
=== Intro Con't === | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Office Scripts VS VBA macros | |||
|- | |||
! Functionality !! Office Scripts !! VBA macros | |||
|- | |||
| '''automating''' solutions through an easy-to-use action '''recorder''' || 1 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| allow '''edits''' of above recordings || 1 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| small programs in Excel by '''not coders''' || 1 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| developed for '''desktop''' solutions || 0 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| designed for secure, cross-platform, '''cloud-based''' solutions || 1 || 0 | |||
|- | |||
| can '''interact''' with a '''user's''' desktop || 0 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| connect with technologies, such as '''COM''' and '''OLE''' || 0 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| have convenient way to call out to the '''internet''' || 1 || 0 | |||
|- | |||
| use a universal '''runtime''' for JavaScript || 1 || 0 | |||
|- | |||
| can make calls to '''web services''' || 1 || 0 | |||
|} | |||
* More about differences here | |||
** <small>https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/resources/vba-differences</small> | |||
* Limited set of available web services (async ways) | |||
** <small>https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/develop/external-calls</small> | |||
== Accessing Scripts == | == Accessing Scripts == | ||
| Line 253: | Line 285: | ||
* also including if the sort column is a Number or String | * also including if the sort column is a Number or String | ||
* if ascending or descending | * if ascending or descending | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="ts"> | |||
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, direct: string, sortType: string, data: schema[]) { | |||
let sortArray: schema[] = []; | |||
if( sortType == "Number" ){ | |||
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => { | |||
if ( direct == "asc" ){ | |||
return a.ID - b.ID; | |||
} else { | |||
return b.ID - a.ID; | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
} else { | |||
if ( direct == "asc" ) { | |||
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => a.ToSort.localeCompare(b.ToSort) ); | |||
} else { | |||
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => b.ToSort.localeCompare(a.ToSort) ); | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
let iRowCount = sortArray.length; | |||
let response: responseType = { | |||
data: sortArray, | |||
total: iRowCount | |||
}; | |||
return sortArray; | |||
} | |||
interface schema { | |||
Date: string; | |||
ToSort: string; | |||
ID: number; | |||
} | |||
interface responseType = { | |||
data: schema[], | |||
total: number | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Additional functions == | == Additional functions == | ||
| Line 271: | Line 342: | ||
*** to test our '''regexps''' - <small>https://regex101.com/</small> | *** to test our '''regexps''' - <small>https://regex101.com/</small> | ||
* more '''functions/constructs''' here - <small>https://www.w3schools.com/js/js_es6.asp</small> | * more '''functions/constructs''' here - <small>https://www.w3schools.com/js/js_es6.asp</small> | ||
== Troubleshooting == | |||
* TS '''restrictions''' in Office Scripts | |||
** https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/develop/typescript-restrictions | |||
* Power Automate contexts | |||
** https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/testing/power-automate-troubleshooting | |||
* Office Scripts '''API''' | |||
** https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/javascript/api/office-scripts/overview?view=office-scripts | |||
== Exercises == | |||
Go to https://myapps.microsoft.com/ | |||
# Create workbook in Excel Online | |||
#* use '''Simple list''' template | |||
#** add new script and call JSONed data from it (-' | |||
#*** HINT: use link from the top of this presu (-8 | |||
#** Count '''how many empty rows''' are there in the current working area? | |||
# Create another workbook in Excel Online | |||
#* use '''Simple service invoice''' | |||
# Yup, yet another workbook (-, | |||
#* Go to https://create.microsoft.com/en-us/search?filters=excel | |||
#* use '''Regional sales chart''' | |||
# Create '''Power Automate''' process | |||
#* use this template with Copilot: | |||
#** "Copy all rows from an Excel file to another excel file with a click of a button" | |||
== Exercises Con't == | |||
# Write data <syntaxhighlight lang="ts" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, param: tab[]) { | |||
let wb = workbook.getWorksheet("Sheet1"); | |||
let rowCount = param.length; | |||
let startRow = 2; | |||
let count = wb.getUsedRange().getRowCount(); | |||
wb.getRange("2:" + count).delete(ExcelScript.DeleteShiftDirection.up); | |||
for (let i = 0; i < param.length; i++) { | |||
const currentObject = param[i]; | |||
const formattedRow = [[currentObject.colA, currentObject.colB, currentObject.colC, currentObject.colD]]; | |||
const rowRange = `A${startRow + i}:D${startRow + i}`; | |||
wb.getRange(rowRange).setValues(formattedRow); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
interface tab { | |||
colA: string; | |||
colB: string; | |||
colC: number; | |||
colD: string; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# Get Data from outside (of a table) <syntaxhighlight lang="ts" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) { | |||
let ws = workbook.getWorksheet("TableData"); | |||
let i=0; | |||
let tab:GetTable[]=[]; | |||
let rng= ws.getRange("a2:d101").getValues(); | |||
let rows = ws.getRange("a2:d101").getRowCount(); | |||
for (i==0; i<rows; i++) { | |||
tab.push({ | |||
text: rng[i][0] as string, | |||
num: rng[i][1] as number, | |||
pers: rng[i][2] as string, | |||
dat: rng[i][3] as string | |||
}) | |||
} | |||
return(tab); | |||
} | |||
interface GetTable{ | |||
text: string, | |||
num: number, | |||
pers: string, | |||
dat: string | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# Get CSV <syntaxhighlight lang="ts" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, csv: string) { | |||
let tab: schema[] = []; | |||
csv = csv.replace(/\r/g, ""); | |||
let rows = csv.split("\n"); | |||
const csvRegex = /(?:,|\n|^)("(?:(?:"")*[^"]*)*"|[^",\n]*|(?:\n|$))/g | |||
rows.forEach((value, index) => { | |||
if (value.length > 0) { | |||
let row = value.match(csvRegex); | |||
if (row[0].charAt(0) === ',') { | |||
row.unshift(""); | |||
} | |||
row.forEach((cell, index) => { | |||
row[index] = cell.indexOf(",") === 0 ? cell.substr(1) : cell; | |||
}); | |||
tab.push( | |||
{ | |||
colA: row[0], | |||
colB: row[1], | |||
colC: row[2], | |||
colD: row[3] | |||
} | |||
); | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
return(tab); | |||
} | |||
interface schema{ | |||
colA: string; | |||
colB: string; | |||
colC: string; | |||
colD: string; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# Regexps <syntaxhighlight lang="ts" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
function main (workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, inputString: string,rgex: string,flag: string) { | |||
let regEx = new RegExp(rgex, flag); | |||
let matches: string[] = []; | |||
let aMatches = inputString.match(regEx); | |||
if (aMatches) { | |||
for (var i = 0; i < aMatches.length; i++) { | |||
matches.push(aMatches[i]); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
return matches; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# Sort Array <syntaxhighlight lang="ts" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, direct:string, sortType: string, data: schema[]) { | |||
let sortArray: schema[] = []; | |||
if(sortType=="Number"){ | |||
sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => { | |||
if (direct=="asc"){ | |||
return a.ID - b.ID; | |||
}else{ | |||
return b.ID - a.ID; | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
} else{ | |||
if (direct == "asc") { | |||
sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => a.ToSort.localeCompare(b.ToSort)); | |||
}else{ | |||
sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => b.ToSort.localeCompare(a.ToSort)); | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
return sortArray | |||
} | |||
interface schema { | |||
Date: string; | |||
ToSort: string; | |||
ID: number; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Latest revision as of 09:25, 28 August 2025
- title
- Power Automate Office Scripts Basics
- author
- Lukasz Sokolowski
Power Automate Office Scripts Basics
Power Automate Office Scripts Basics Training Materials
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2004-2026 by NobleProg Limited All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and permission must be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise.
Agenda
Single module context
- Accessing Scripts
- Triggering Scripts in Power Automate
- IntelliSense
- Variables, Types and Interfaces
- If
- Loop
- Get & Set
- Basic Excel Actions
- Send and Return Data
- Additional functions
- Troubleshooting
- Exercises
Introduction
Office Scripts
- Online version of VBA
- Built to run in Excel Online
- similar to GoogleDocs App Scripts, but based on TypeScript instead of Javascript
- TS is a subset of JS, so we can use JS as well
- Office Scripts are only available for Excel (no support in Outlook, Word, Access, etc)
- for both - Online and Windows versions of excel
- More here
Intro Con't
| Functionality | Office Scripts | VBA macros |
|---|---|---|
| automating solutions through an easy-to-use action recorder | 1 | 1 |
| allow edits of above recordings | 1 | 1 |
| small programs in Excel by not coders | 1 | 1 |
| developed for desktop solutions | 0 | 1 |
| designed for secure, cross-platform, cloud-based solutions | 1 | 0 |
| can interact with a user's desktop | 0 | 1 |
| connect with technologies, such as COM and OLE | 0 | 1 |
| have convenient way to call out to the internet | 1 | 0 |
| use a universal runtime for JavaScript | 1 | 0 |
| can make calls to web services | 1 | 0 |
- More about differences here
- Limited set of available web services (async ways)
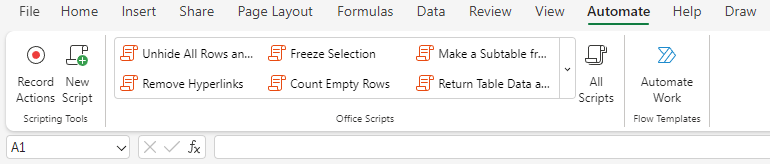
Accessing Scripts
In Excel online (Business version only)
- an Automate tab in the ribbon bar
- the Ribbon allows to record actions (just like vba)
- Create a blank New Script
- Open existing Scripts
- and Automate a Task with a Power Automate template
- The Record function
- does not record every action
- uses selections instead of references
- does show good notes and is a good way to learn
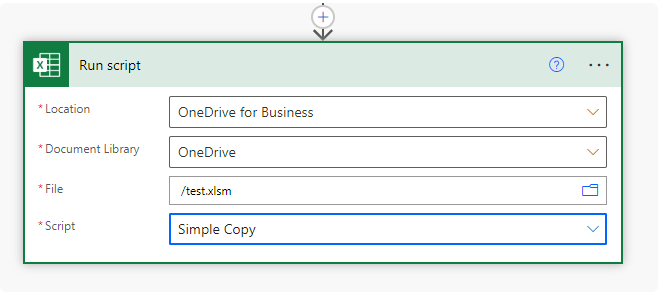
Triggering Scripts in Power Automate
Office Scripts
- can be run by adding the Run script action under Excel Online (Business)
- More here (connector docs)
- by default stored on our OneDrive (Documents/Office Scripts folder)
- can be shared with a file by clicking Share (same menu as adding a button)
- this attaches the script to the file, so anyone with the file can run the script
- unfortunately shared scripts can not be called by Power Automate
- it can only call scripts stored on the connected OneDrive account
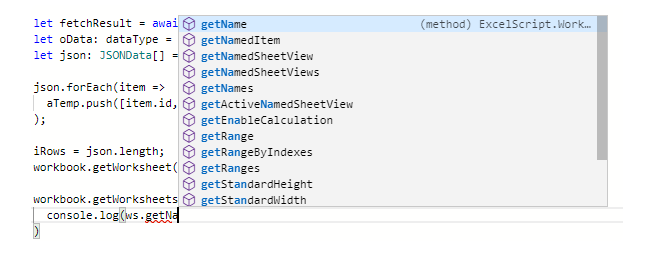
IntelliSense
Intellisense
- auto complete for code
- we type in the function we want
- Office Scripts will try and guess what we're typing by listing all possible options
- speeding up our typing
- can be used as a reference to find the function we're looking for
Variables, Types and Interfaces
Basic TypeScript knowledge is required
- variables are declared with let or const
- need to declare type (must have value set against them)
let sString = "";
let iNumber = 0;
let bFlag = false;
- we declare objects like: workbooks, worksheets, images, ranges and more to variables
- make them easier to use and update
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let ws = workbook.getWorksheet("Sheet1");
ws.setName("test");
}
- variables are scoped locally
- declared in the function/loop is scoped to that function/loop only
- can't be read outside of it
Arrays, interfaces
2 options, an empty array and structured one
- Empty arrays - for simple arrays with no objects within them
- If we need an object - we should use an interface to set the structure
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbooklet){
let aSimple = []; // [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
let aStructured: Schema[];
/* [ { stringField:"test", numberField:1, booleanField: false }
, { stringField:"test2", numberField:2, booleanField:true } ] */
}
interface Schema {
stringField: string,
numberField: number,
booleanField: boolean
}
Types vs Interfaces
type is for an object
- for structuring an object we're about to add to an array
- usually is also called outside of the function
- similar to an interface, but less general
- interface - reusable but generic, usually outlives the module
- type - reusable but more specific, usually stays within the module
type dataType = {
data: JSONData[]
}
If
Fundamental action
- Office Scripts leverage TypeScript/JavaScript
- Logic is different to Excel
- equals is ==
- === also matches type -
5 == "5"is true,5 === "5"is false
- === also matches type -
- not equals is !=
- greater then and less then are standard ( >, <, >=, <= )
- we can also just pass a boolean in or an array to see if it is not empty
- equals is ==
- Examples
// full
if( rng[i][0] == 7 ){
aNewRange.push( rng[i] );
} else {
console.log( "Not a 7" );
}
// simple
let bFlag = true
if( bFlag ){
console.log( "works as a charm" );
}
// ternary
invVoided ? 'voided' : 'stays'
Loops
- for
for( i = 0; i < rng.length; i++ ){
//do something
}
- for ... in, for ... of
for ( let cell of row ) {
if ( cell.toString().length > 0 ) {
emptyRow = false;
}
}
- forEach
workbook.getWorksheets().forEach( ws => console.log( ws.getName() ) )
Get & Set
.getWorkSheet("Sheet1")
- get is used to reference something
- to either store as variable or to complete an action against e.g. setValue()
- it can get not only parts of the workbook, but parameters to them, like worksheet name
- we get our worksheet, get our range, then we set our range
- that can be a formula (setFormula) or value (setValue)
- can be one cell or a range (setValues)
Example
- Copying a filtered list from one sheet to another
// First thought - the best approach would be to filter the excel data, then copy and paste
//// Better is to grab the whole range, filter it, then paste and set the range to the filtered values
// We could also set the range 'row by row' in the loop
//// - but this can have a big impact on performance
//// - for any interactions with the Excel, file uses api calls
//// - we should avoid placing them in loops where ever possible
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let ws = workbook.getWorksheet( "summary" );
let i = 0;
let aNewRange = [];
let rng = ws.getUsedRange().getValues(); // gets values from range
aNewRange.push( rng[0] ); // adds header row
for( i == 0; i < rng.length; i++ ){ // loops over rows in the array
if( rng[i][0]==3 ){ // if condition
aNewRange.push( rng[i] ); // adds row to array
}
}
// sets array to range
workbook.getWorksheet( "Sheet2" )
.getRange( "A1:e"+aNewRange.length )
.setValues( aNewRange );
}
Basic Excel Actions
We can interact with the Excel workbook
let ws= workbook.addWorksheet("test"); // Add worksheet called 'test'
ws.delete(); // Delete worksheet
// Insert chart on sheet 'selectedSheet'
let chartName = selectedSheet.addChart(ExcelScript.ChartType.pie, selectedSheet.getRange("A1:C15"));
// Add a new pivot table on 'sheet3'
let newPivotTable = workbook.addPivotTable("PivotTableName", ws.getRange("A1:C15"), wsPivot.getRange("A2:C16"))
newPivotTable.refresh(); // Refresh newPivotTable
// Apply values filter of 1 to range
ws.getAutoFilter().apply(ws.getAutoFilter().getRange(), 0, { filterOn: ExcelScript.FilterOn.values, values: ["1"] });
// Add thin border to bottom of range
ws.getRange("A1:C4").getFormat().getRangeBorder(ExcelScript.BorderIndex.edgeBottom).setWeight(ExcelScript.BorderWeight.thin);
ws.getRange("A1:C4").getFormat().getFill().setColor("FFFF00"); // Set fill color to 'FFFF00' for range
ws.getRange("A1:C4").removeDuplicates([0], false); // Remove duplicates from range 'A1:C4'
// Insert column F:F, move existing cells right
ws.getRange("F:F").insert(ExcelScript.InsertShiftDirection.right);
ws.getRange("F:F").delete(ExcelScript.DeleteShiftDirection.left); // Delete column F:F
ws.getRange("3:3").insert(ExcelScript.InsertShiftDirection.down); // Insert at range 3:3, move existing cells down
ws.getRange("3:3").delete(ExcelScript.DeleteShiftDirection.up); // Delete row 3:3
Send and Return Data
Office Scripts become Power Automate Scripts
- We can pass
- multiple parameters in
- and one out
- though this can be an object or array (then it can be multiple parameters too)
- There are couple of limits to the connector
- request and response size being 5MB (Excel online)
- maximum size of parameters passed to the Run script action - 28.6MB (Power Automate)
- more here - https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dev/scripts/testing/platform-limits?tabs=business
Example
Passing an array that we want to sort
- also including if the sort column is a Number or String
- if ascending or descending
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, direct: string, sortType: string, data: schema[]) {
let sortArray: schema[] = [];
if( sortType == "Number" ){
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => {
if ( direct == "asc" ){
return a.ID - b.ID;
} else {
return b.ID - a.ID;
}
});
} else {
if ( direct == "asc" ) {
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => a.ToSort.localeCompare(b.ToSort) );
} else {
sortArray = data.sort( (a, b) => b.ToSort.localeCompare(a.ToSort) );
}
};
let iRowCount = sortArray.length;
let response: responseType = {
data: sortArray,
total: iRowCount
};
return sortArray;
}
interface schema {
Date: string;
ToSort: string;
ID: number;
}
interface responseType = {
data: schema[],
total: number
}
Additional functions
Office Scripts are TypeScript/JavaScript
- most of JavaScript functions are available
- few examples:
- .sort() - Sort Array
- Example - Sort
- .filter() - Filter Array
- .includes() - Find in Array
- Example - Includes
- .matchAll() - Search in String
- Example - matchAll
- .match(), .search(), .test(), .replace(), .exec() - Regexp Patterns
- Example - Test
- References - https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/jsref_obj_regexp.asp
- to test our regexps - https://regex101.com/
- .sort() - Sort Array
- more functions/constructs here - https://www.w3schools.com/js/js_es6.asp
Troubleshooting
- TS restrictions in Office Scripts
- Power Automate contexts
- Office Scripts API
Exercises
Go to https://myapps.microsoft.com/
- Create workbook in Excel Online
- use Simple list template
- add new script and call JSONed data from it (-'
- HINT: use link from the top of this presu (-8
- Count how many empty rows are there in the current working area?
- add new script and call JSONed data from it (-'
- use Simple list template
- Create another workbook in Excel Online
- use Simple service invoice
- Yup, yet another workbook (-,
- Go to https://create.microsoft.com/en-us/search?filters=excel
- use Regional sales chart
- Create Power Automate process
- use this template with Copilot:
- "Copy all rows from an Excel file to another excel file with a click of a button"
- use this template with Copilot:
Exercises Con't
- Write data
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, param: tab[]) { let wb = workbook.getWorksheet("Sheet1"); let rowCount = param.length; let startRow = 2; let count = wb.getUsedRange().getRowCount(); wb.getRange("2:" + count).delete(ExcelScript.DeleteShiftDirection.up); for (let i = 0; i < param.length; i++) { const currentObject = param[i]; const formattedRow = [[currentObject.colA, currentObject.colB, currentObject.colC, currentObject.colD]]; const rowRange = `A${startRow + i}:D${startRow + i}`; wb.getRange(rowRange).setValues(formattedRow); } } interface tab { colA: string; colB: string; colC: number; colD: string; }
- Get Data from outside (of a table)
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) { let ws = workbook.getWorksheet("TableData"); let i=0; let tab:GetTable[]=[]; let rng= ws.getRange("a2:d101").getValues(); let rows = ws.getRange("a2:d101").getRowCount(); for (i==0; i<rows; i++) { tab.push({ text: rng[i][0] as string, num: rng[i][1] as number, pers: rng[i][2] as string, dat: rng[i][3] as string }) } return(tab); } interface GetTable{ text: string, num: number, pers: string, dat: string }
- Get CSV
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, csv: string) { let tab: schema[] = []; csv = csv.replace(/\r/g, ""); let rows = csv.split("\n"); const csvRegex = /(?:,|\n|^)("(?:(?:"")*[^"]*)*"|[^",\n]*|(?:\n|$))/g rows.forEach((value, index) => { if (value.length > 0) { let row = value.match(csvRegex); if (row[0].charAt(0) === ',') { row.unshift(""); } row.forEach((cell, index) => { row[index] = cell.indexOf(",") === 0 ? cell.substr(1) : cell; }); tab.push( { colA: row[0], colB: row[1], colC: row[2], colD: row[3] } ); } }); return(tab); } interface schema{ colA: string; colB: string; colC: string; colD: string; }
- Regexps
function main (workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, inputString: string,rgex: string,flag: string) { let regEx = new RegExp(rgex, flag); let matches: string[] = []; let aMatches = inputString.match(regEx); if (aMatches) { for (var i = 0; i < aMatches.length; i++) { matches.push(aMatches[i]); } } return matches; }
- Sort Array
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook, direct:string, sortType: string, data: schema[]) { let sortArray: schema[] = []; if(sortType=="Number"){ sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => { if (direct=="asc"){ return a.ID - b.ID; }else{ return b.ID - a.ID; } }); } else{ if (direct == "asc") { sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => a.ToSort.localeCompare(b.ToSort)); }else{ sortArray = data.sort((a, b) => b.ToSort.localeCompare(a.ToSort)); } }; return sortArray } interface schema { Date: string; ToSort: string; ID: number; }