WebServices: Difference between revisions
Lsokolowski (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 19:42, 26 June 2018
<slideshow style="nobleprog" headingmark="⌘" incmark="…" scaled="true" font="Trebuchet MS" >
- title
- Web Services Basics For Non-programmers
- author
- Pete George (NobleProg Ltd)
</slideshow>
Day One Schedule ⌘
- Introductions
- Service-Oriented Architecture
- Web Services Overview
- XML
- SOAP
Web Services Overview ⌘
Learning Objectives
- To understand what a Web service is
- To be aware of the development of Web services
- To understand the reasons for the popularity of Web services
- To be aware of the existence of Web service standards
Web Services Definition ⌘
“a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network.” (W3C)
“a means to connect services together.” (Barry, 2013)
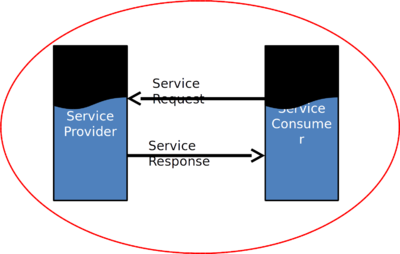
Web Service Architecture ⌘
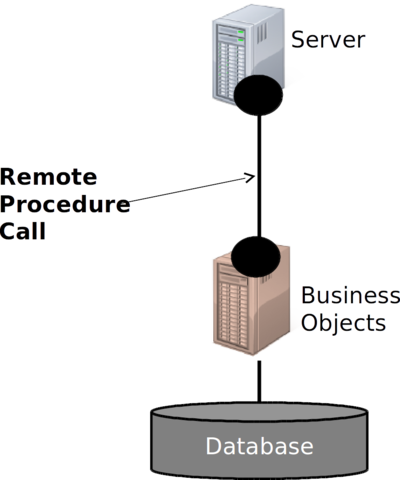
Remote Procedure Call (RPC)⌘
RPC Protocols ⌘
Protocols, e.g. DCOM, specify:

- What address of target computer looks like
- How data should be packaged
- How response is retrieved
- How to initiate call
- How to handle errors
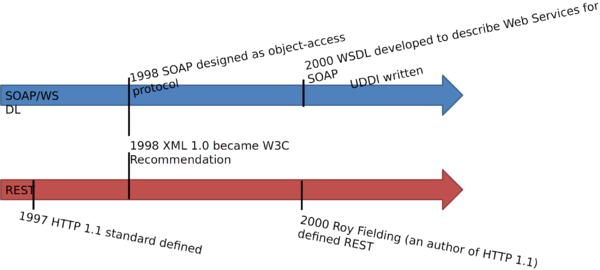
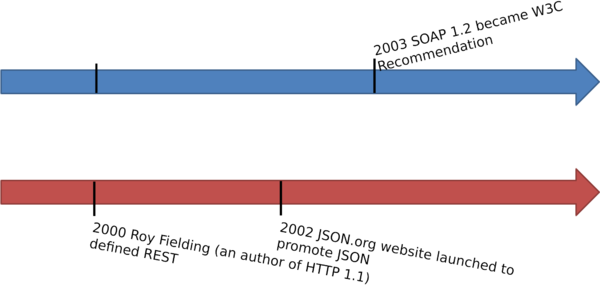
Web Services History ⌘
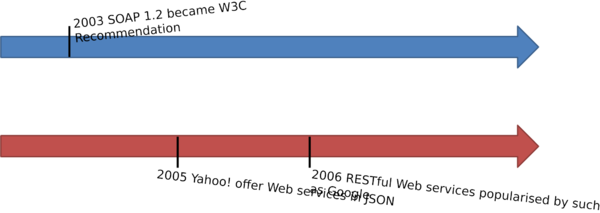
Web Services History 1 ⌘
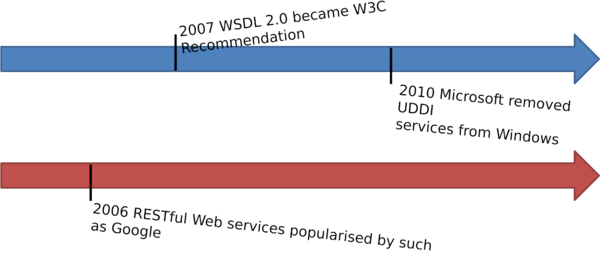
Web Services History 2 ⌘
Web Services History 3 ⌘
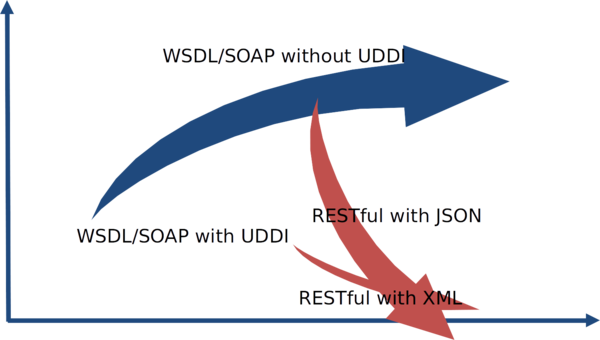
Web Services Today ⌘
Which Type of Web Service? ⌘
- Best for your development environment
- Used most by services you will use
- Used most by external services you will use
- All of the above
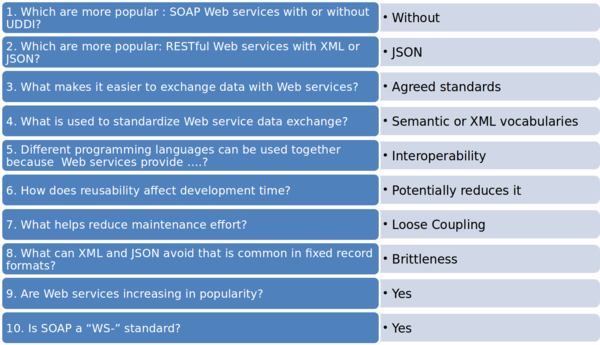
Why are Web Services Popular? ⌘
- Business benefits
- Development benefits
- Snowball effect
Why are Web Services Popular? ⌘
- Business benefits
-Easier exchange of data
-Industry-wide standards
-More external services available to all
-Efficient merging of systems (e.g. in acquisitions)
Easier Data Exchange ⌘
- Data elements are sent in addition to value
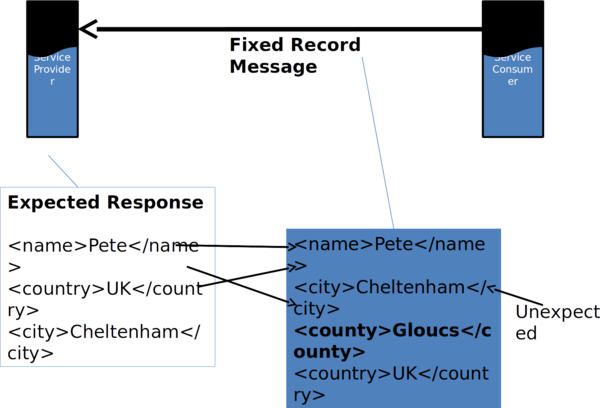
- XML:
-<element>value</element>
-E.g. <city>Liverpool</city>
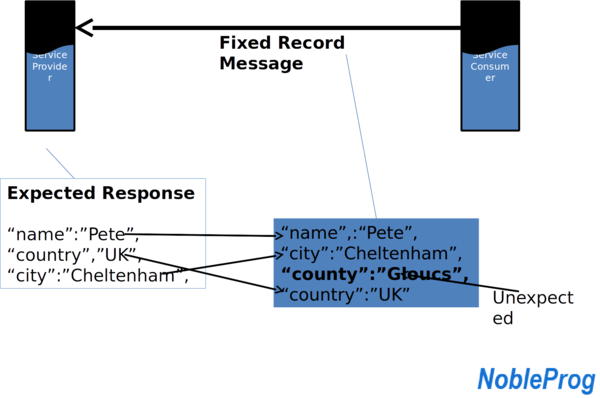
- JSON
-“element” : “value”
-E.g. “city”:”Liverpool”
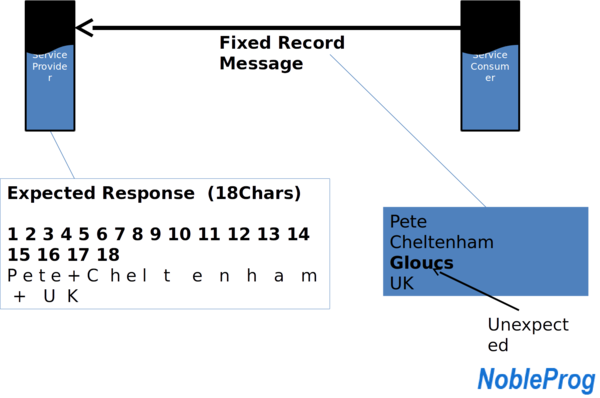
What About Mismatches? ⌘
- Application 1:
-<city>Liverpool</city>
-<town>Cheltenham</town>
- Application 2:
-<city>Liverpool</city>
-<city>Cheltenham</city>
Agreed Data Exchange Standards ⌘
- Minimize development costs
- Minimize processing errors
Semantic Vocabularies ⌘
- Also known as XML Vocabularies
- NB: both XML and JSON can use the same vocabularies/elements
-<city>Liverpool</city>
-“city”: “Liverpool”
Industry-Wide Standards ⌘
- Web services created opportunity to establish industry-wide standardized vocabularies
- Two types:
-Common Semantic Vocabularies
-Specific Semantic Vocabularies
Common Semantic Vocabularies ⌘
- EXAMPLES
- Mail.XML
-XML specification for communication.
- eXtensible Customer Relationships Language
-XML standard specification to represent customer relationships in a standard way.
- Open Office XML
-OpenDocument Format (ODF). Open XML-based document file format for office applications.
Specific Semantic Vocabularies ⌘
- EXAMPLES
- Flexible Image Transport System Markup Language (FITSML)
-Astronomy XML specification
- HR-XML
-Human Resources XML specification
- DocBook
-XML vocabulary for Publishing industry
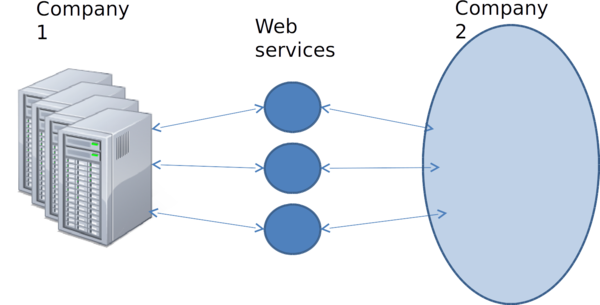
More External Services Available ⌘
Merging Systems ⌘
Why are Web Services Popular? ⌘
- Development benefits
-Interoperability
-Reduced development time
-Reduced maintenance
-Reduced brittleness
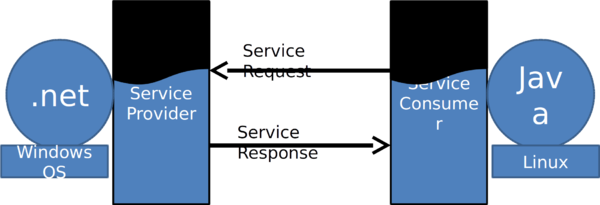
Interoperability ⌘
Reduced Development Time ⌘
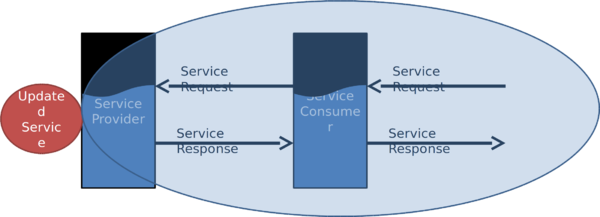
Reduced Maintenance ⌘
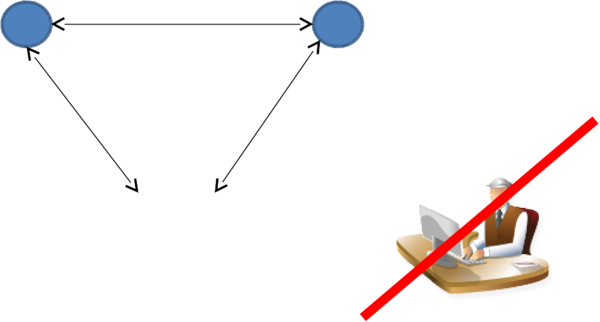
Brittleness ⌘
Reduced Brittleness XML ⌘
Reduced Brittleness JSON ⌘
Why are Web Services Popular? ⌘
- Snowball effect
-Popularity of Web services forced vendors to include in their products
- More Web services in products increases popularity
-Popularity of Web services ….
-Popularity of Web services create demand for training and tools
- More training and tools increases popularity of Web services
-Popularity of Web services…
“WS-” Specifications ⌘
- No single defined set or governing body for Web service specifications
- “WS-” = shorthand for Web service specifications
-WS-Security, WS-Discovery et al
-SOAP
-XML
-etc